Parental bonding in males with adjustment disorder and hyperventilation syndrome
- PMID: 22672223
- PMCID: PMC3425085
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-244X-12-56
Parental bonding in males with adjustment disorder and hyperventilation syndrome
Abstract
Background: The purpose of the study was to identify the style of parental bonding and the personality characteristics that might increase the risk of hyperventilation and adjustment disorder.
Methods: A total of 917 males were recruited, 156 with adjustment disorder and hyperventilation syndrome (AD + HY), 273 with adjustment disorder without hyperventilation syndrome (AD-HY), and 488 healthy controls. All participants completed the Parental Bonding Instrument, Eysenck Personality Questionnaire, and Chinese Health Questionnaire.
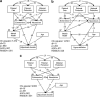
Results: Analysis using structural equation models identified a pathway relationship in which parental bonding affected personality characteristics, personality characteristics affected mental health condition, and mental health condition affected the development of hyperventilation or adjustment disorder. Males with AD-HY perceived less paternal care, and those with AD + HY perceived more maternal protection than those with adjustment disorder and those in the control group. Participants with AD-HY were more neurotic and less extroverted than those with AD + HY. Both groups showed poorer mental health than the controls.
Conclusions: Although some patients with hyperventilation syndrome demonstrated symptoms of adjustment disorder, there were different predisposing factors between the two groups in terms of parental bonding and personality characteristics. This finding is important for the early intervention and prevention of hyperventilation and adjustment disorder.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Parental attachment, premorbid personality, and mental health in young males with hyperventilation syndrome.Psychiatry Res. 2007 Oct 31;153(2):163-70. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2006.05.006. Epub 2007 Jul 30. Psychiatry Res. 2007. PMID: 17659783
-
Perceived Parental Bonding, Early Maladaptive Schemas and Outcome in Schema Therapy of Cluster C Personality Problems.Clin Psychol Psychother. 2016 Mar-Apr;23(2):107-17. doi: 10.1002/cpp.1938. Epub 2014 Nov 25. Clin Psychol Psychother. 2016. PMID: 25425509
-
Sub-optimal parenting is associated with schizotypic and anxiety personality traits in adulthood.Eur Psychiatry. 2013 May;28(4):254-60. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpsy.2012.07.002. Epub 2012 Oct 10. Eur Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 23062835
-
Association between different types of childhood trauma and parental bonding with antisocial traits in adulthood: A systematic review.Child Abuse Negl. 2020 Sep;107:104621. doi: 10.1016/j.chiabu.2020.104621. Epub 2020 Jun 27. Child Abuse Negl. 2020. PMID: 32603957
-
Parental affectionless control and suicidality.J Affect Disord. 2013 Oct;151(1):1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2013.05.096. Epub 2013 Jun 29. J Affect Disord. 2013. PMID: 23820097 Review.
References
-
- Lung FW, Lee FY, Shu BC. The relationship between life adjustment and parental bonding in military personnel with adjustment disorder in Taiwan. Mil Med. 2002;167:678–682. - PubMed
-
- Lung FW, Lee FY, Shu BC. The premorbid personality in military students with adjustment disorder. Mil Psychol. 2006;18:77–88. doi: 10.1207/s15327876mp1801_5. - DOI
-
- Parker G. Parental overprotection: a risk factor in psychosocial development. Grune & Stratton, New York; 1983.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

