Time course of depression and one-year prognosis of patients with stroke in mainland China
- PMID: 22672300
- PMCID: PMC6493639
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2012.00312.x
Time course of depression and one-year prognosis of patients with stroke in mainland China
Abstract
Aims: To investigate the incidence of depression at different time points within the first year after stroke in mainland China and to identify risk factors related to a poor 1-year prognosis in stroke patients.
Methods: Subjects with acute cerebrovascular diseases were recruited and enrolled from 56 hospitals in mainland China between April 2008 and April 2010. Demographic data, previous disease history, and clinical data were collected. Four follow-up visits were occurred within the first year after stroke. The modified Rankin Scale ≥ 2 represents an unfavorable prognosis. Depression was diagnosed according to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, fourth edition and was divided into persistent, recurrent and transient types.
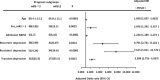
Results: The 1-year cumulative incidence of depression in stroke patients was 41.8%. Logistic regression analysis showed that the 1-year prognosis level was associated with age, disability before onset, neurological functional deficit level at admission, and a range of depression types. The odds ratio for persistent depression is the highest (OR = 7.615, P < 0.0001, 95% confidence interval 5.011-11.572).
Conclusions: In our study, depression occurred in >40% of patients within the first year after stroke. Persistent depression is the first independent determinant of prognosis during the first year after stroke.
© 2012 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hadidi N, Treat‐Jacobson DJ, Lindquist R. Poststroke depression and functional outcome: A critical review of literature. Heart Lung. 2009;38:151–162. - PubMed
-
- Haas DC, Davidson KW, Schwartz DJ, et al Depressive symptoms are independently predictive of carotid atherosclerosis. Am J Cardiol 2005;95:547–550. - PubMed
-
- Aström M, Adolfsson R, Asplund K. Major depression in stroke patients. A 3‐year longitudinal study. Stroke 1993;24:976–982. - PubMed
-
- Kouwenhoven SE, Kirkevold M, Engedal K, Kim HS. Depression in acute stroke: Prevalence, dominant symptoms and associated factors. A systematic literature review. Disabil Rehabil 2011;33:539–556. - PubMed
-
- Kauhanen M, Korpelainen JT, Hiltunen P, et al Poststroke depression correlates with cognitive impairment and neurological deficits. Stroke 1999;30:1875–1880. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

