NPY intraperitoneal injections produce antidepressant-like effects and downregulate BDNF in the rat hypothalamus
- PMID: 22672302
- PMCID: PMC6493532
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2012.00314.x
NPY intraperitoneal injections produce antidepressant-like effects and downregulate BDNF in the rat hypothalamus
Abstract
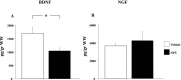
Aims: Several studies have documented an involvement of Neuropeptide Y (NPY) in stress-related disorders. Stress-related disorders are also characterized by changes in brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and nerve growth factor (NGF), neurotrophins implicated in the survival and function of neurons. Thus the aim of this study was to investigate whether an NPY intraperitoneal treatment has antidepressant-like effects in rats subjected to a classical stress paradigm, the Forced Swim Test (FST), in association with changes in local brain neurotrophin production.
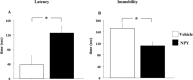
Methods: Rats were intraperitoneally injected with either NPY (60 μg/kg) or a vehicle for three consecutive days between two FST sessions and then tested for time spent (or delay onset) in immobile posture. Moreover, we measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) neurotrophin levels in the hypothalamus and corticosterone levels in plasma.
Results: The data showed that NPY induced a significant delay in the onset and a significant reduction in the duration of the immobility posture in FST. We also found that NPY decreased BDNF levels in the hypothalamus and corticosterone levels in plasma.
Discussion: Immobility posture in FST can be reduced by antidepressant drugs. Thus, our data show an antidepressant-like effect of NPY associated with changes in BDNF levels in the hypothalamus and reduced activity of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis.
Conclusion: These findings, while confirming the involvement of the NPY system in stress-related disorders, suggest that a less invasive route of administration, such as an intraperitoneal injection, may be instrumental in coping with stressful events in animal models and perhaps in humans.
© 2012 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Paschos KA, Veletza S, Chatzaki E. Neuropeptide and sigma receptors as novel therapeutic targets for the pharmacotherapy of depression. CNS Drugs 2009;23:755–772. - PubMed
-
- Redrobe JP, Dumont Y, Quirion R. Neuropeptide Y (NPY) and depression: From animal studies to the human condition. Life Sci 2002;71:2921–2937. - PubMed
-
- Heilig M. The NPY system in stress, anxiety and depression. Neuropeptides 2004;38:213–224. - PubMed
-
- Jiménez‐Vasquez PA, Diaz‐Cabiale Z, Caberlotto L, Bellido I, Overstreet D, Fuxe K, Mathé AA. Electroconvulsive stimuli selectively affect behavior and neuropeptide Y (NPY) and NPY Y(1) receptor gene expressions in hippocampus and hypothalamus of Flinders Sensitive Line rat model of depression. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 2007;17:298–308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

