Co-ordinate regulation of cytokinin gene family members during flag leaf and reproductive development in wheat
- PMID: 22672647
- PMCID: PMC3410795
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2229-12-78
Co-ordinate regulation of cytokinin gene family members during flag leaf and reproductive development in wheat
Abstract
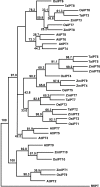
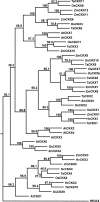
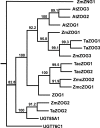
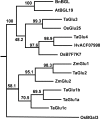
Background: As the global population continues to expand, increasing yield in bread wheat is of critical importance as 20% of the world's food supply is sourced from this cereal. Several recent studies of the molecular basis of grain yield indicate that the cytokinins are a key factor in determining grain yield. In this study, cytokinin gene family members in bread wheat were isolated from four multigene families which regulate cytokinin synthesis and metabolism, the isopentenyl transferases (IPT), cytokinin oxidases (CKX), zeatin O-glucosyltransferases (ZOG), and β-glucosidases (GLU). As bread wheat is hexaploid, each gene family is also likely to be represented on the A, B and D genomes. By using a novel strategy of qRT-PCR with locus-specific primers shared among the three homoeologues of each family member, detailed expression profiles are provided of family members of these multigene families expressed during leaf, spike and seed development.
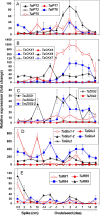
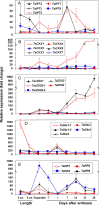
Results: The expression patterns of individual members of the IPT, CKX, ZOG, and GLU multigene families in wheat are shown to be tissue- and developmentally-specific. For instance, TaIPT2 and TaCKX1 were the most highly expressed family members during early seed development, with relative expression levels of up to 90- and 900-fold higher, respectively, than those in the lowest expressed samples. The expression of two cis-ZOG genes was sharply increased in older leaves, while an extremely high mRNA level of TaGLU1-1 was detected in young leaves.
Conclusions: Key genes with tissue- and developmentally-specific expression have been identified which would be prime targets for genetic manipulation towards yield improvement in bread wheat breeding programmes, utilising TILLING and MAS strategies.
Figures


References
-
- International Grains Council. Grain Market report. 2010. [ www.igc.int/downloads/gmrsummary/gmrsumme.pdf]
-
- FAO. FAOSTAT. 2010. [ http://faostat.fao.org/site/368/DesktopDefault.aspx?PageID=368#ancor]
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

