Add-on aliskiren elicits stronger renoprotection than high-dose valsartan in type 2 diabetic KKAy mice that do not respond to low-dose valsartan
- PMID: 22673148
- PMCID: PMC3396743
- DOI: 10.1254/jphs.12031fp
Add-on aliskiren elicits stronger renoprotection than high-dose valsartan in type 2 diabetic KKAy mice that do not respond to low-dose valsartan
Abstract
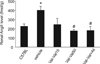
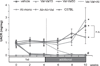
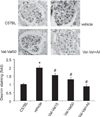
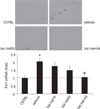
We hypothesized that aliskiren provides renoprotection in diabetic animals that did not receive sufficient renoprotection by AT1-receptor antagonist treatment. Type 2 diabetic KKAy mice were treated with group 1: vehicle or group 2: valsartan (15 mg/kg per day) from 12 to 16 weeks of age. The mice were subsequently divided into 4 groups and treated with the following combinations of drugs for another 6 weeks: 1: group 1 kept receiving vehicle, 2: group 2 continuously received 15 mg/kg per day of valsartan (Val-Val15), 3: group 2 received 50 mg/kg per day of valsartan (Val-Val50), 4: group 2 continuously received 15 mg/kg per day of valsartan with 25 mg/kg per day of aliskiren (Val-Val+Ali). Aliskiren exerted significant anti-albuminuric effects, whereas valsartan failed to ameliorate the albuminuria in the first four weeks. Surprisingly, the increasing dosage of valsartan in the Val-Val50 group showed non-significant tendencies to attenuate the albuminuria compared with vehicle infusion. Val-Val+Ali significantly suppressed the development of albuminuria and podocyte injury. Val-Val50 and Val-Val+Ali showed similar suppression of angiotensin II contents in the kidney of KKAy mice. In conclusion, the anti-albuminuric effect that was observed in the type 2 diabetic mice showing no anti-albuminuric effect by valsartan can be attributed to the add-on aliskiren.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aliskiren, a human renin inhibitor, ameliorates cardiac and renal damage in double-transgenic rats.Hypertension. 2005 Sep;46(3):569-76. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000179573.91016.3f. Epub 2005 Aug 15. Hypertension. 2005. PMID: 16103264
-
Aliskiren enhances the protective effects of valsartan against cardiovascular and renal injury in endothelial nitric oxide synthase-deficient mice.Hypertension. 2009 Sep;54(3):633-8. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.109.133884. Epub 2009 Jul 13. Hypertension. 2009. PMID: 19597038
-
Hemodynamic and hormonal changes to dual renin-angiotensin system inhibition in experimental hypertension.Hypertension. 2013 Feb;61(2):417-24. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.112.201889. Epub 2012 Dec 10. Hypertension. 2013. PMID: 23232645 Free PMC article.
-
Aliskiren and valsartan combination therapy for the management of hypertension.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2010 Sep 7;6:711-22. doi: 10.2147/vhrm.s8175. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2010. PMID: 20859542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Azilsartan, aliskiren, and combination antihypertensives utilizing renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system antagonists.Am J Ther. 2014 Sep-Oct;21(5):419-35. doi: 10.1097/MJT.0b013e31824a0ed7. Am J Ther. 2014. PMID: 22975662 Review.
Cited by
-
Angiotensin II blockade and renal protection.Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(17):3033-42. doi: 10.2174/1381612811319170009. Curr Pharm Des. 2013. PMID: 23176216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A mouse model of renal fibrosis to overcome the technical variability in ischaemia/reperfusion injury among operators.Sci Rep. 2019 Jul 18;9(1):10435. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-46994-z. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31320707 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor does not suppress renal angiotensin II levels in angiotensin I-infused rats.J Pharmacol Sci. 2013;122(2):103-8. doi: 10.1254/jphs.13045fp. Epub 2013 May 22. J Pharmacol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23698111 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting senescence to prevent diabetic kidney disease: Exploring molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets for disease management.Diabet Med. 2025 Feb;42(2):e15408. doi: 10.1111/dme.15408. Epub 2024 Jul 12. Diabet Med. 2025. PMID: 38995865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of the Angiotensin receptor blocker olmesartan on adipocyte hypertrophy and function in mice with metabolic disorders.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:946492. doi: 10.1155/2014/946492. Epub 2014 Jun 2. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 24991574 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boor P, Floege J. Chronic kidney disease growth factors in renal fibrosis. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2011;38:391–400. - PubMed

