Proinflammatory actions of glucocorticoids: glucocorticoids and TNFα coregulate gene expression in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 22673229
- PMCID: PMC3404340
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2012-1020
Proinflammatory actions of glucocorticoids: glucocorticoids and TNFα coregulate gene expression in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
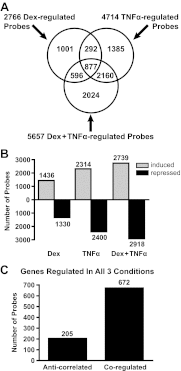
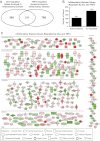
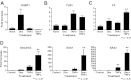
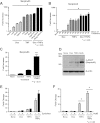
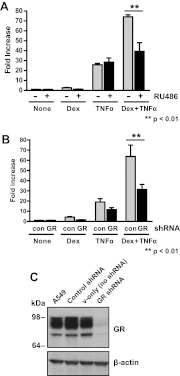
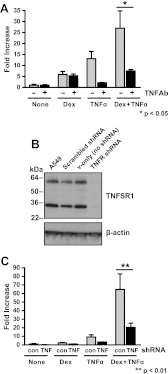
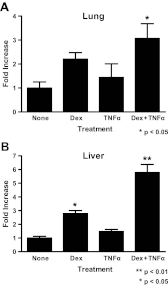
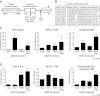
Synthetic glucocorticoids are widely used for treatment of many inflammatory diseases. However, long-term glucocorticoid treatment can cause a variety of negative side effects. A genome-wide microarray analysis was performed in human lung A549 cells to identify genes regulated by both the antiinflammatory steroid dexamethasone (Dex) and the proinflammatory cytokine TNFα. Unexpectedly, we discovered that numerous genes were coregulated by treatment with both Dex and TNFα. We evaluated the mechanism of coregulation of one of these genes, serpinA3 (α-1 antichymotrypsin), a secreted, acute phase protein strongly associated with numerous inflammatory diseases. Up-regulation of serpinA3 requires the presence of both the glucocorticoid receptor and TNFα soluble receptor 1. Treatment with Dex or TNFα resulted in a 10- to 25-fold increase of serpinA3 mRNA, whereas coadministration of Dex and TNFα led to a synergistic increase in serpinA3 mRNA. The naturally occurring glucocorticoid, cortisol, also resulted in a synergistic increase in serpinA3 mRNA levels in A549 cells. Furthermore, in vivo treatment of C57BL/6 mice with Dex and TNFα resulted in coregulation of serpinA3 mRNA levels in both lung and liver tissues. Finally, chromatin immunoprecipitation analyses suggest that glucocorticoid receptor binding to the serpinA3 transcriptional start site can be enhanced by the combination of Dex plus TNFα treatment of A549 cells. These studies demonstrate that glucocorticoids and proinflammatory compounds can coregulate genes associated with human disease. This discovery may underlie the basis of some of the adverse effects associated with long-term glucocorticoid therapy.
Figures
References
-
- Revollo JR, Cidlowski JA. 2009. Mechanisms generating diversity in glucocorticoid receptor signaling. Ann NY Acad Sci 1179:167–178 - PubMed
-
- Baschant U, Tuckermann J. 2010. The role of the glucocorticoid receptor in inflammation and immunity. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 120:69–75 - PubMed
-
- Magnussen H, Watz H. 2009. Systemic inflammation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma: relation with comorbidities. Proc Am Thorac Soc 6:648–651 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

