Anti-angiogenic therapy increases intratumoral adenovirus distribution by inducing collagen degradation
- PMID: 22673390
- PMCID: PMC3443547
- DOI: 10.1038/gt.2012.42
Anti-angiogenic therapy increases intratumoral adenovirus distribution by inducing collagen degradation
Abstract
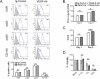
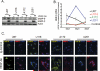
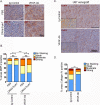
Conditionally replicating adenoviruses (CRAd) are a promising class of gene therapy agents that can overcome already known glioblastoma (GBM) resistance mechanisms but have limited distribution upon direct intratumoral (i.t.) injection. Collagen bundles in the extracellular matrix (ECM) have an important role in inhibiting virus distribution. In fact, ECM pre-treatment with collagenases improves virus distributions to tumor cells. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are an endogenous class of collagenases secreted by tumor cells whose function can be altered by different drugs including anti-angiogenic agents, such as bevacizumab. In this study we hypothesized that upregulation of MMP activity during anti-angiogenic therapy can improve CRAd-S-pk7 distribution in GBM. We find that MMP-2 activity in human U251 GBM xenografts increases (*P=0.03) and collagen IV content decreases (*P=0.01) during vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF-A) antibody neutralization. After proving that collagen IV inhibits CRAd-S-pk7 distribution in U251 xenografts (Spearman rho=-0.38; **P=0.003), we show that VEGF-blocking antibody treatment followed by CRAd-S-pk7 i.t. injection reduces U251 tumor growth more than each individual agent alone (***P<0.0001). Our data propose a novel approach to improve virus distribution in tumors by relying on the early effects of anti-angiogenic therapy.
Figures



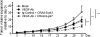
References
-
- Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Taphoorn MJ, Janzer RC, et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10(5):459–66. - PubMed
-
- Ulasov IV, Zhu ZB, Tyler MA, Han Y, Rivera AA, Khramtsov A, et al. Survivin-driven and fiber-modified oncolytic adenovirus exhibits potent antitumor activity in established intracranial glioma. Hum Gene Ther. 2007;18(7):589–602. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

