A statistical modeling approach for evaluating auto-segmentation methods for image-guided radiotherapy
- PMID: 22673541
- PMCID: PMC3398201
- DOI: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2012.05.001
A statistical modeling approach for evaluating auto-segmentation methods for image-guided radiotherapy
Abstract
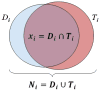
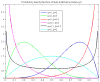
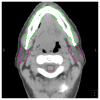
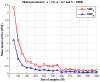
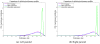
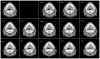
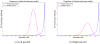
We proposed a statistical modeling method for the quantitative evaluation of segmentation methods used in image guided radiotherapy. A statistical model parameterized on a Beta distribution was built upon the observations of the volume overlap between the segmented structure and the referenced structure. A statistical performance profile (SPP) was then estimated from the model using the generalized maximum likelihood approach. The SPP defines the probability density function characterizing the distribution of performance values and provides a graphical visualization of the segmentation performance. Different segmentation approaches may be influenced by image quality or observer variability. Our statistical model was able to quantify the impact of these variations and displays the underlying statistical performance of the segmentation algorithm. We demonstrated the efficacy of this statistical model using both simulated data and clinical evaluation studies in head and neck radiotherapy. Furthermore, the resulting SPP facilitates the measurement of the correlation between quantitative metrics and clinical experts' decision, and ultimately is able to guide the clinicians in selecting segmentation methods for radiotherapy.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding the work presented here.
Figures
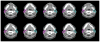
References
-
- Ezzell GA, Galvin JM, Low D, Palta JR, Rosen I, Sharpe MB, Xia P, Xiao Y, Xing L, Yu CX. Guidance document on delivery, treatment planning, and clinical implementation of IMRT: Report of the IMRT subcommittee of the AAPM radiation therapy committee. Medical Physics. 2003;30:2089–2115. - PubMed
-
- Mackie TR, Kapatoes J, Ruchala K, Lu W, Wu C, Olivera G, Forrest L, Tome W, Welsh J, Jeraj R, Harari P, Reckwerdt P, Paliwal B, Ritter M, Keller H, Fowler J, Mehta M. Image guidance for precise conformal radiotherapy. International Journal of Radiation Oncology * Biology * Physics. 2003;56:89–105. - PubMed
-
- Cozzi L, Fogliata A, Bolsi A, Nicolini G, Bernier J. Three-dimensional conformal vs. intensity-modulated radiotherapy in head-and-neck cancer patients: Comparative analysis of dosimetric and technical parameters. International Journal of Radiation Oncology * Biology * Physics. 2004;58:617–624. - PubMed
-
- Chao KSC, Bhide S, Chen H, Asper J, Bush S, Franklin G, Kavadi V, Liengswangwong V, Gordon W, Raben A, Strasser J, Koprowski C, Frank S, Chronowski G, Ahamad A, Malyapa R, Zhang L, Dong L. Reduce in Variation and Improve Efficiency of Target Volume Delineation by a Computer-Assisted System Using a Deformable Image Registration Approach. International Journal of Radiation Oncology * Biology * Physics. 2007;68:1512–1521. - PubMed
-
- Stapleford LJ, Lawson JD, Perkins C, Edelman S, Davis L, McDonald MW, Waller A, Schreibmann E, Fox T. Evaluation of Automatic Atlas-Based Lymph Node Segmentation for Head-and-Neck Cancer. International Journal of Radiation Oncology * Biology * Physics. 2010;77:959–966. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

