Genomic variation in natural populations of Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 22673804
- PMCID: PMC3454882
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.112.142018
Genomic variation in natural populations of Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
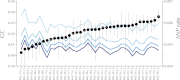
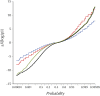
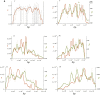
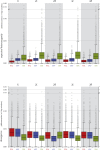
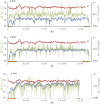
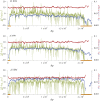
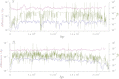
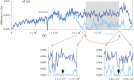
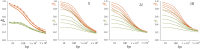
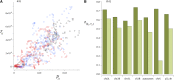
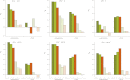
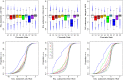
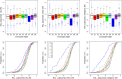
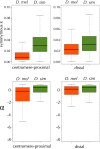
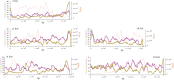
This report of independent genome sequences of two natural populations of Drosophila melanogaster (37 from North America and 6 from Africa) provides unique insight into forces shaping genomic polymorphism and divergence. Evidence of interactions between natural selection and genetic linkage is abundant not only in centromere- and telomere-proximal regions, but also throughout the euchromatic arms. Linkage disequilibrium, which decays within 1 kbp, exhibits a strong bias toward coupling of the more frequent alleles and provides a high-resolution map of recombination rate. The juxtaposition of population genetics statistics in small genomic windows with gene structures and chromatin states yields a rich, high-resolution annotation, including the following: (1) 5'- and 3'-UTRs are enriched for regions of reduced polymorphism relative to lineage-specific divergence; (2) exons overlap with windows of excess relative polymorphism; (3) epigenetic marks associated with active transcription initiation sites overlap with regions of reduced relative polymorphism and relatively reduced estimates of the rate of recombination; (4) the rate of adaptive nonsynonymous fixation increases with the rate of crossing over per base pair; and (5) both duplications and deletions are enriched near origins of replication and their density correlates negatively with the rate of crossing over. Available demographic models of X and autosome descent cannot account for the increased divergence on the X and loss of diversity associated with the out-of-Africa migration. Comparison of the variation among these genomes to variation among genomes from D. simulans suggests that many targets of directional selection are shared between these species.
Figures
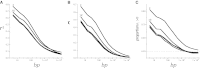


References
-
- Adams M. D., Celniker S. E., Holt C. A., Evans J. D., Gocayne J. D., et al. , 2000. The genome sequence of Drosophila melanogaster. Science 287: 2185–2195 - PubMed
-
- Aguadé M., Meyers W., Long A. D., Langley C. H., 1994. Single-strand conformation polymorphism analysis coupled with stratified DNA sequencing reveals reduced sequence variation in the su(s) and su(wa) regions of the Drosophila melanogaster X chromosome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91: 4658–4662 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

