Abrogation of lectin-like oxidized LDL receptor-1 attenuates acute myocardial ischemia-induced renal dysfunction by modulating systemic and local inflammation
- PMID: 22673889
- PMCID: PMC4045456
- DOI: 10.1038/ki.2012.186
Abrogation of lectin-like oxidized LDL receptor-1 attenuates acute myocardial ischemia-induced renal dysfunction by modulating systemic and local inflammation
Abstract
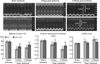
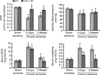
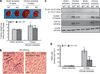
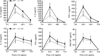
It is assumed that acute myocardial infarction affects renal function. To study the mechanism, we used mice following permanent ligation of their left coronary artery that results in extensive myocardial infarction. Soon after ligation, there was a marked rise in circulating pro-inflammatory cytokines and malondialdehyde (thiobarbituric acid-positive evidence of lipid peroxidation). Renal function had significantly declined by the third day in association with mild fibrosis, and swelling of glomeruli and tubules. There was a significant increase in the expression of the lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 (LOX-1), interelukin-1β, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1, and thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances in the kidney. Renal function showed some recovery by Day 21; however, there was progressive fibrosis of the kidneys. LOX-1 knockout mice had significantly diminished increases in systemic and renal pro-inflammatory cytokines, malondialdehyde, structural alterations, and decline in renal function than the wild-type mice following ligation of the left coronary artery. Cardiac function and survival rates were also significantly better in the LOX-1 knockout mice than in the wild-type mice. Hence, severe myocardial ischemia results in renal dysfunction and histological abnormalities suggestive of acute renal injury. Thus, LOX-1 is a key modulator among multiple mechanisms underlying renal dysfunction following extensive myocardial infarction.
Figures


References
-
- Ronco C, Haapio M, House AA, et al. Cardiorenal syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;52:1527–1539. - PubMed
-
- Shlipak MG, Massie BM. The clinical challenge of cardiorenal syndrome. Circulation. 2004;110:1514–1517. - PubMed
-
- Gobal F, Deshmukh A, Shah S, et al. Triad of metabolic syndrome, chronic kidney disease, and coronary heart disease with a focus on microalbuminuria death by overeating. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;57:2303–2308. - PubMed
-
- van Kimmenade RR, Pinto Y, Januzzi JL., Jr When renal and cardiac insufficiencies intersect: is there a role for natriuretic peptide testing in the ‘cardio-renal syndrome’? Eur Heart J. 2007;28:2960–2961. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

