Taming lupus-a new understanding of pathogenesis is leading to clinical advances
- PMID: 22674006
- PMCID: PMC3607103
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.2752
Taming lupus-a new understanding of pathogenesis is leading to clinical advances
Abstract
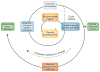
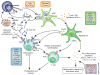
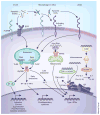
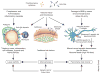
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease that is characterized by the loss of tolerance to nuclear self antigens, the production of pathogenic autoantibodies and damage to multiple organ systems. Over the years, patients with SLE have been managed largely with empiric immunosuppressive therapies, which are associated with substantial toxicities and do not always provide adequate control of the disease. The development of targeted therapies that specifically address disease pathogenesis or progression has lagged, largely because of the complex and heterogeneous nature of the disease, as well as difficulties in designing uniform outcome measures for clinical trials. Recent advances that could improve the treatment of SLE include the identification of genetic variations that influence the risk of developing the disease, an enhanced understanding of innate and adaptive immune activation and regulation of tolerance, dissection of immune cell activation and inflammatory pathways and elucidation of mechanisms and markers of tissue damage. These discoveries, together with improvements in clinical trial design, form a platform from which to launch the development of a new generation of lupus therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING FINANCIAL INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Lateef A, Petri M. Biologics in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2010;22:504–509. - PubMed
-
- Navarra SV, et al. Efficacy and safety of belimumab in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus: a randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2011;377:721–731. - PubMed
-
- Lauwerys BR, Wakeland EK. Genetics of lupus nephritis. Lupus. 2005;14:2–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

