Signaling from the adherens junction
- PMID: 22674072
- PMCID: PMC4031758
- DOI: 10.1007/978-94-007-4186-7_8
Signaling from the adherens junction
Abstract
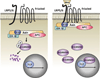
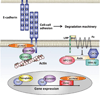
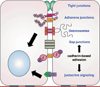
The cadherin/catenin complex organizes to form a structural Velcro that joins the cytoskeletal networks of adjacent cells. Functional loss of this complex arrests the development of normal tissue organization, and years of research have gone into teasing out how the physical structure of adhesions conveys information to the cell interior. Evidence that most cadherin-binding partners also localize to the nucleus to regulate transcription supports the view that cadherins serve as simple stoichiometric inhibitors of nuclear signals. However, it is also clear that cadherin-based adhesion initiates a variety of molecular events that can ultimately impact nuclear signaling. This chapter discusses these two modes of cadherin signaling in the context of tissue growth and differentiation.
Figures



References
-
- Andrade MA, Petosa C, O’Donoghue SI, Muller CW, Bork P. Comparison of ARM and HEAT protein repeats. J Mol Biol. 2001;309:1–18. - PubMed
-
- Behrens J, von Kries JP, Kuhl M, Bruhn L, Wedlich D, Grosschedl R, Birchmeier W. Functional interaction of beta-catenin with the transcription factor LEF-1. Nature. 1996;382:638–642. - PubMed
-
- Berx G, Becker KF, Hofler H, van Roy F. Mutations of the human E-cadherin (CDH1) gene. Hum Mutat. 1998;12:226–237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

