STAT3-iNOS Signaling Mediates EGFRvIII-Induced Glial Proliferation and Transformation
- PMID: 22674257
- PMCID: PMC3409246
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3243-11.2012
STAT3-iNOS Signaling Mediates EGFRvIII-Induced Glial Proliferation and Transformation
Abstract
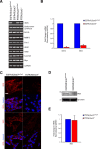
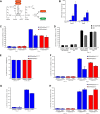
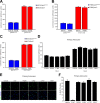
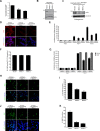
Malignant gliomas, including glioblastoma multiforme, constitute the most common and aggressive primary brain tumors in adults. The transcription factor signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) plays an essential role in glioblastoma pathogenesis downstream of the major oncogenic protein epidermal growth factor receptor variant III (EGFRvIII). However, the critical gene targets of STAT3 that mediate EGFRvIII-induced glial transformation have remained unknown. Here, we identify inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) as a novel target gene of STAT3 in EGFRvIII-expressing mouse astrocytes. Endogenous STAT3 occupies the endogenous iNOS promoter and stimulates iNOS transcription in EGFRvIII-expressing astrocytes. STAT3 does not appear to control iNOS transcription in astrocytes deficient in the major glioblastoma tumor suppressor protein phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN), suggesting that STAT3 regulates iNOS transcription specifically in EGFRvIII-expressing astrocytes. Importantly, inhibition of iNOS by distinct approaches, including knockdown by RNA interference, reduces cell population growth and invasiveness of EGFRvIII-expressing astrocytes. In addition, upon iNOS knockdown or administration of a small-molecule inhibitor of iNOS, EGFRvIII-expressing astrocytes form smaller tumors in vivo. These findings suggest that inhibition of iNOS may have potential therapeutic value for EGFRvIII-activated brain tumors.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification of a PTEN-regulated STAT3 brain tumor suppressor pathway.Genes Dev. 2008 Feb 15;22(4):449-62. doi: 10.1101/gad.1606508. Epub 2008 Feb 7. Genes Dev. 2008. PMID: 18258752 Free PMC article.
-
Deregulation of a STAT3-interleukin 8 signaling pathway promotes human glioblastoma cell proliferation and invasiveness.J Neurosci. 2008 Jun 4;28(23):5870-8. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5385-07.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18524891 Free PMC article.
-
iNOS: a potential therapeutic target for malignant glioma.Curr Mol Med. 2013 Sep;13(8):1241-9. doi: 10.2174/1566524011313080002. Curr Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23590833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
JAK2/STAT3 targeted therapy suppresses tumor invasion via disruption of the EGFRvIII/JAK2/STAT3 axis and associated focal adhesion in EGFRvIII-expressing glioblastoma.Neuro Oncol. 2014 Sep;16(9):1229-43. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nou046. Epub 2014 May 25. Neuro Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24861878 Free PMC article.
-
Ribozyme-mediated inhibition of 801-bp deletion-mutant epidermal growth factor receptor mRNA expression in glioblastoma multiforme.Molecules. 2010 Jun 30;15(7):4670-8. doi: 10.3390/molecules15074670. Molecules. 2010. PMID: 20657384 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pam2 lipopeptides enhance the immunosuppressive activity of monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells by STAT3 signal in chronic inflammation.Cent Eur J Immunol. 2022;47(1):30-40. doi: 10.5114/ceji.2022.113086. Epub 2022 Feb 11. Cent Eur J Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35600157 Free PMC article.
-
Microglia-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Reduce Glioma Growth by Modifying Tumor Cell Metabolism and Enhancing Glutamate Clearance through miR-124.Cells. 2021 Aug 12;10(8):2066. doi: 10.3390/cells10082066. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34440835 Free PMC article.
-
Single-Cell Transcriptomic Analysis of Primary and Metastatic Tumor Ecosystems in Head and Neck Cancer.Cell. 2017 Dec 14;171(7):1611-1624.e24. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.10.044. Epub 2017 Nov 30. Cell. 2017. PMID: 29198524 Free PMC article.
-
Cell line with endogenous EGFRvIII expression is a suitable model for research and drug development purposes.Oncotarget. 2016 May 31;7(22):31907-25. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8201. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27004406 Free PMC article.
-
The Role and Therapeutic Targeting of JAK/STAT Signaling in Glioblastoma.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jan 24;13(3):437. doi: 10.3390/cancers13030437. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33498872 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akaike T, Yoshida M, Miyamoto Y, Sato K, Kohno M, Sasamoto K, Miyazaki K, Ueda S, Maeda H. Antagonistic action of imidazolineoxyl N-oxides against endothelium-derived relaxing factor/.NO through a radical reaction. Biochemistry. 1993;32:827–832. - PubMed
-
- Aoki Y, Feldman GM, Tosato G. Inhibition of STAT3 signaling induces apoptosis and decreases survivin expression in primary effusion lymphoma. Blood. 2003;101:1535–1542. - PubMed
-
- Bachoo RM, Maher EA, Ligon KL, Sharpless NE, Chan SS, You MJ, Tang Y, DeFrances J, Stover E, Weissleder R, Rowitch DH, Louis DN, DePinho RA. Epidermal growth factor receptor and Ink4a/Arf: convergent mechanisms governing terminal differentiation and transformation along the neural stem cell to astrocyte axis. Cancer Cell. 2002;1:269–277. - PubMed
-
- Bajenaru ML, Hernandez MR, Perry A, Zhu Y, Parada LF, Garbow JR, Gutmann DH. Optic nerve glioma in mice requires astrocyte Nf1 gene inactivation and Nf1 brain heterozygosity. Cancer Res. 2003;63:8573–8577. - PubMed
-
- Bonni A, Sun Y, Nadal-Vicens M, Bhatt A, Frank DA, Rozovsky I, Stahl N, Yancopoulos GD, Greenberg ME. Regulation of gliogenesis in the central nervous system by the JAK-STAT signaling pathway. Science. 1997;278:477–483. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
