Neurotoxicity and memory deficits induced by soluble low-molecular-weight amyloid-β1-42 oligomers are revealed in vivo by using a novel animal model
- PMID: 22674261
- PMCID: PMC6620963
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5901-11.2012
Neurotoxicity and memory deficits induced by soluble low-molecular-weight amyloid-β1-42 oligomers are revealed in vivo by using a novel animal model
Abstract
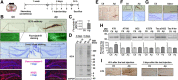
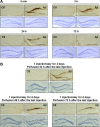
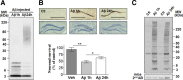
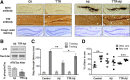
Neuronal and synaptic degeneration are the best pathological correlates for memory decline in Alzheimer's disease (AD). Although the accumulation of soluble low-molecular-weight amyloid-β (Aβ) oligomers has been suggested to trigger neurodegeneration in AD, animal models overexpressing or infused with Aβ lack neuronal loss at the onset of memory deficits. Using a novel in vivo approach, we found that repeated hippocampal injections of small soluble Aβ(1-42) oligomers in awake, freely moving mice were able to induce marked neuronal loss, tau hyperphosphorylation, and deficits in hippocampus-dependent memory. The neurotoxicity of small Aβ(1-42) species was observed in vivo as well as in vitro in association with increased caspase-3 activity and reduced levels of the NMDA receptor subunit NR2B. We found that the sequestering agent transthyretin is able to bind the toxic Aβ(1-42) species and attenuated the loss of neurons and memory deficits. Our novel mouse model provides evidence that small, soluble Aβ(1-42) oligomers are able to induce extensive neuronal loss in vivo and initiate a cascade of events that mimic the key neuropathological hallmarks of AD.
Figures



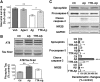
References
-
- AbdAlla S, Lother H, el Missiry A, Langer A, Sergeev P, el Faramawy Y, Quitterer U. Angiotensin II AT2 receptor oligomers mediate G-protein dysfunction in an animal model of Alzheimer disease. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:6554–6565. - PubMed
-
- Arendt T. Synaptic degeneration in Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2009;118:167–179. - PubMed
-
- Benilova I, Karran E, De Strooper B. The toxic Aβ oligomer and Alzheimer's disease: an emperor in need of clothes. Nat Neurosci. 2012;15:349–357. - PubMed
-
- Broersen K, Jonckheere W, Rozenski J, Vandersteen A, Pauwels K, Pastore A, Rousseau F, Schymkowitz J. A standardized and biocompatible preparation of aggregate-free amyloid beta peptide for biophysical and biological studies of Alzheimer's disease. Protein Eng Des Sel. 2011;24:743–750. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
