Highly efficient and exact method for parallelization of grid-based algorithms and its implementation in DelPhi
- PMID: 22674480
- PMCID: PMC3412928
- DOI: 10.1002/jcc.23033
Highly efficient and exact method for parallelization of grid-based algorithms and its implementation in DelPhi
Abstract
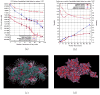
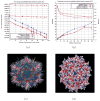
The Gauss-Seidel (GS) method is a standard iterative numerical method widely used to solve a system of equations and, in general, is more efficient comparing to other iterative methods, such as the Jacobi method. However, standard implementation of the GS method restricts its utilization in parallel computing due to its requirement of using updated neighboring values (i.e., in current iteration) as soon as they are available. Here, we report an efficient and exact (not requiring assumptions) method to parallelize iterations and to reduce the computational time as a linear/nearly linear function of the number of processes or computing units. In contrast to other existing solutions, our method does not require any assumptions and is equally applicable for solving linear and nonlinear equations. This approach is implemented in the DelPhi program, which is a finite difference Poisson-Boltzmann equation solver to model electrostatics in molecular biology. This development makes the iterative procedure on obtaining the electrostatic potential distribution in the parallelized DelPhi several folds faster than that in the serial code. Further, we demonstrate the advantages of the new parallelized DelPhi by computing the electrostatic potential and the corresponding energies of large supramolecular structures.
Copyright © 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Nicholls A, Honig B. Journal of computational chemistry. 1991;12(4):435–445.
-
- Gilson MK, Rashin A, Fine R, Honig B. Journal of molecular biology. 1985;184(3):503–516. - PubMed
-
- Luo R, David L, Gilson MK. Journal of computational chemistry. 2002;23(13):1244–1253. - PubMed
-
- Hsieh MJ, Luo R. Proteins: Structure, Function, and Bioinformatics. 2004;56(3):475–486. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

