Breast tomosynthesis and digital mammography: a comparison of diagnostic accuracy
- PMID: 22674710
- PMCID: PMC3500806
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr/53282892
Breast tomosynthesis and digital mammography: a comparison of diagnostic accuracy
Abstract
Objective: Our aim was to compare the ability of radiologists to detect breast cancers using one-view breast tomosynthesis (BT) and two-view digital mammography (DM) in an enriched population of diseased patients and benign and/or healthy patients.
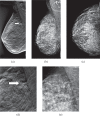
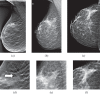
Methods: All participants gave informed consent. The BT and DM examinations were performed with about the same average glandular dose to the breast. The study population comprised patients with subtle signs of malignancy seen on DM and/or ultrasonography. Ground truth was established by pathology, needle biopsy and/or by 1-year follow-up by mammography, which retrospectively resulted in 89 diseased breasts (1 breast per patient) with 95 malignant lesions and 96 healthy or benign breasts. Two experienced radiologists, who were not participants in the study, determined the locations of the malignant lesions. Five radiologists, experienced in mammography, interpreted the cases independently in a free-response study. The data were analysed by the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) and jackknife alternative free-response ROC (JAFROC) methods, regarding both readers and cases as random effects.
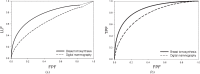
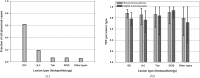
Results: The diagnostic accuracy of BT was significantly better than that of DM (JAFROC: p=0.0031, ROC: p=0.0415). The average sensitivity of BT was higher than that of DM (∼90% vs ∼79%; 95% confidence interval of difference: 0.036, 0.108) while the average false-positive fraction was not significantly different (95% confidence interval of difference: -0.117, 0.010).
Conclusion: The diagnostic accuracy of BT was superior to DM in an enriched population.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The diagnostic accuracy of dual-view digital mammography, single-view breast tomosynthesis and a dual-view combination of breast tomosynthesis and digital mammography in a free-response observer performance study.Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2010 Apr-May;139(1-3):113-7. doi: 10.1093/rpd/ncq044. Epub 2010 Mar 12. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2010. PMID: 20228048 Free PMC article.
-
Digital breast tomosynthesis as an adjunct to digital mammography for detecting and characterising invasive lobular cancers: a multi-reader study.Clin Radiol. 2016 Sep;71(9):889-95. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2016.04.004. Epub 2016 Jun 6. Clin Radiol. 2016. PMID: 27210245
-
Comparison of the diagnostic performance of digital breast tomosynthesis and magnetic resonance imaging added to digital mammography in women with known breast cancers.Eur Radiol. 2016 Jun;26(6):1556-64. doi: 10.1007/s00330-015-3998-3. Epub 2015 Sep 16. Eur Radiol. 2016. PMID: 26376882
-
Breast tomosynthesis: Accuracy of tumor measurement compared with digital mammography and ultrasonography.Acta Radiol. 2010 Apr;51(3):240-7. doi: 10.3109/02841850903524447. Acta Radiol. 2010. PMID: 20105090
-
Tomosynthesis-detected Architectural Distortion: Management Algorithm with Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation.Radiographics. 2016 Mar-Apr;36(2):311-21. doi: 10.1148/rg.2016150093. Radiographics. 2016. PMID: 26963448 Review.
Cited by
-
Digital breast tomosynthesis within a symptomatic "one-stop breast clinic" for characterization of subtle findings.Br J Radiol. 2015 Sep;88(1053):20140855. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20140855. Epub 2015 Jul 2. Br J Radiol. 2015. PMID: 26133221 Free PMC article.
-
Conspicuity of suspicious breast lesions on contrast enhanced breast CT compared to digital breast tomosynthesis and mammography.Br J Radiol. 2019 May;92(1097):20181034. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20181034. Epub 2019 Apr 3. Br J Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30810339 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology of Breast Cancer - Current Figures and Trends.Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 2013 Feb;73(2):130-135. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1328075. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 2013. PMID: 24771909 Free PMC article.
-
Breast cancer detection in digital breast tomosynthesis and digital mammography-a side-by-side review of discrepant cases.Br J Radiol. 2014 Aug;87(1040):20140080. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20140080. Epub 2014 Jun 4. Br J Radiol. 2014. PMID: 24896197 Free PMC article.
-
One-view digital breast tomosynthesis as a stand-alone modality for breast cancer detection: do we need more?Eur Radiol. 2018 May;28(5):1938-1948. doi: 10.1007/s00330-017-5167-3. Epub 2017 Dec 11. Eur Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29230524 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Socialstyrelsen.se [homepage on the Internet]. Stockholm, Sweden: Swedish National Board of Health and Welfare; Cancer Incidence in Sweden 2008 [cited 9 July 2011]. Available from: www.socialstyrelsen.se/publikationer2009/2009-12-1.
-
- Laming D, Warren R. Improving the detection of cancer in the screening of mammograms. J Med Screen 2000;7:24–30 - PubMed
-
- Kolb TM, Lichy J, Newhouse JH. Comparison of the performance of screening mammography, physical examination, and breast US and evaluation of factors that influence them: an analysis of 27 825 patient evaluations. Radiol 2002;225:165–75 - PubMed
-
- Skaane P. Studies comparing screen-film mammography and full-field digital mammography in breast cancer screening: updated review. Acta Radiol 2009;50:503–14 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

