Metabotropic actions of the volatile anaesthetic sevoflurane increase protein kinase M synthesis and induce immediate preconditioning protection of rat hippocampal slices
- PMID: 22674720
- PMCID: PMC3476650
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2012.233965
Metabotropic actions of the volatile anaesthetic sevoflurane increase protein kinase M synthesis and induce immediate preconditioning protection of rat hippocampal slices
Abstract
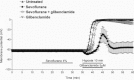
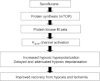
Anaesthetic preconditioning occurs when a volatile anaesthetic, such as sevoflurane, is administered before a hypoxic or ischaemic insult; this has been shown to improve neuronal recovery after the insult. We found that sevoflurane-induced preconditioning in the rat hippocampal slice enhances the hypoxic hyperpolarization of CA1 pyramidal neurons, delays and attenuates their hypoxic depolarization, and increases the number of neurons that recover their resting and action potentials after hypoxia. These altered electrophysiological effects and the improved recovery corresponded with an increase in the amount of a constitutively active, atypical protein kinase C isoform found in brain, protein kinase M zeta (PKMζ). A selective inhibitor of this kinase, zeta inhibitory peptide (ZIP), blocked the increase in the total amount of PKMζ protein and the amount of the activated form of this kinase, phospho-PKMζ (p-PKMζ); it also blocked the altered electrophysiological effects and the improved recovery. We found that both cycloheximide, a general protein synthesis inhibitor, and rapamycin, a selective inhibitor of the mTOR pathway for regulating protein synthesis, blocked the increase in p-PKMζ, the electrophysiological changes, and the improved recovery due to sevoflurane-induced preconditioning. Glibenclamide, a KATP channel blocker, when present only during the hypoxia, prevented the enhanced hyperpolarization, the delayed and attenuated hypoxic depolarization, and the improved recovery following sevoflurane-induced preconditioning. To examine the function of persistent PKMζ and KATP channel activity after the preconditioning was established, we administered 4% sevoflurane for 30 min and then discontinued it for 30 min before 10 min of hypoxia. When either tolbutamide, a KATP channel blocker, or ZIP were administered at least 15 min after the washout of sevoflurane, there was little recovery compared with sevoflurane alone. Thus, continuous KATP channel and PKMζ activity are required to maintain preconditioning protection. We conclude that sevoflurane induces activation of the mTOR pathway, increasing the new protein synthesis of PKMζ, which is constitutively phosphorylated to its active form, leading to an increased KATP channel-induced hyperpolarizaton. This hyperpolarization delays and attenuates the hypoxic depolarization, improving the recovery of neurons following hypoxia. Thus, sevoflurane acts via a metabotropic pathway to improve recovery following hypoxia.
Figures






References
-
- Aronow HD, Gray WA, Ramee SR, Mishkel GJ, Schreiber TJ, Wang H. Predictors of Neurological Events Associated With Carotid Artery Stenting in High-Surgical-Risk Patients: Insights From the Cordis Carotid Stent Collaborative. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2010;3:577–584. - PubMed
-
- Arsham AM, Howell JJ, Simon MC. A novel hypoxia-inducible factor-independent hypoxic response regulating mammalian target of rapamycin and its targets. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:29655–29660. - PubMed
-
- Bickler PE, Warner DS, Stratmann G, Schuyler JA. gamma-Aminobutyric acid-A receptors contribute to isoflurane neuroprotection in organotypic hippocampal cultures. Anesthesia and analgesia. 2003;97:564–571. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

