A new method to efficiently induce a site-specific double-strand break in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe
- PMID: 22674789
- PMCID: PMC3389596
- DOI: 10.1002/yea.2908
A new method to efficiently induce a site-specific double-strand break in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe
Abstract
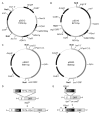
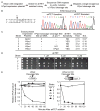
Double-strand DNA breaks are a serious threat to cellular viability and yeast systems have proved invaluable in helping to understand how these potentially toxic lesions are sensed and repaired. An important method to study the processing of DNA breaks in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae is to introduce a unique double-strand break into the genome by regulating the expression of the site-specific HO endonuclease with a galactose inducible promoter. Variations of the HO site-specific DSB assay have been adapted to many organisms, but the methodology has seen only limited use in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe because of the lack of a promoter capable of inducing endonuclease expression on a relatively short time scale (~1 h). We have overcome this limitation by developing a new assay in which expression of the homing endonuclease I-PpoI is tightly regulated with a tetracycline-inducible promoter. We show that induction of the I-PpoI endonuclease produces rapid cutting of a defined cleavage site (> 80% after 1 h), efficient cell cycle arrest and significant accumulation of the checkpoint protein Crb2 at break-adjacent regions in a manner that is analogous to published findings with DSBs produced by an acute exposure to ionizing irradiation. This assay provides an important new tool for the fission yeast community and, because many aspects of mammalian chromatin organization have been well-conserved in Sz. pombe but not in S. cerevisiae, also offers an attractive system to decipher the role of chromatin structure in modulating the repair of double-stranded DNA breaks.
Copyright © 2012 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures



References
-
- Bahler J, Wu JQ, Longtine MS, et al. Heterologous modules for efficient and versatile PCR-based gene targeting in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Yeast. 1998;14:943–951. - PubMed
-
- Berkovich E, Monnat RJJ, Kastan MB. Roles of ATM and NBS1 in chromatin structure modulation and DNA double-strand break repair. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9:683–690. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
