Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity against primary HIV-infected CD4+ T cells is directly associated with the magnitude of surface IgG binding
- PMID: 22674985
- PMCID: PMC3421757
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00287-12
Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity against primary HIV-infected CD4+ T cells is directly associated with the magnitude of surface IgG binding
Abstract
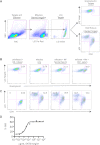
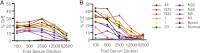
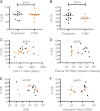
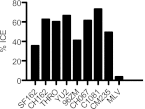
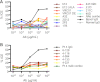
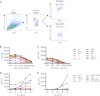
Antibody (Ab)-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) is thought to potentially play a role in vaccine-induced protection from HIV-1. The characteristics of such antibodies remain incompletely understood. Furthermore, correlates between ADCC and HIV-1 immune status are not clearly defined. We screened the sera of 20 HIV-1-positive (HIV-1(+)) patients for ADCC. Normal human peripheral blood mononuclear cells were used to derive HIV-infected CD4(+) T cell targets and autologous, freshly isolated, natural killer (NK) cells in a novel assay that measures granzyme B (GrB) and HIV-1-infected CD4(+) T cell elimination (ICE) by flow cytometry. We observed that complex sera mediated greater levels of ADCC than anti-HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein (Env)-specific monoclonal antibodies and serum-mediated ADCC correlated with the amount of IgG and IgG1 bound to HIV-1-infected CD4(+) T cells. No correlation between ADCC and viral load, CD4(+) T cell count, or neutralization of HIV-1(SF162) or other primary viral isolates was detected. Sera pooled from clade B HIV-1(+) individuals exhibited breadth in killing targets infected with HIV-1 from clades A/E, B, and C. Taken together, these data suggest that the total amount of IgG bound to an HIV-1-infected cell is an important determinant of ADCC and that polyvalent antigen-specific Abs are required for a robust ADCC response. In addition, Abs elicited by a vaccine formulated with immunogens from a single clade may generate a protective ADCC response in vivo against a variety of HIV-1 species. Increased understanding of the parameters that dictate ADCC against HIV-1-infected cells will inform efforts to stimulate ADCC activity and improve its potency in vaccinees.
Figures
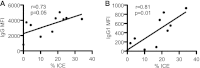
References
-
- Ahmad R, et al. 2001. Evidence for a correlation between antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity-mediating anti-HIV-1 antibodies and prognostic predictors of HIV infection. J. Clin. Immunol. 21:227–233 - PubMed
-
- Baum LL, et al. 1996. HIV-1 gp120-specific antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity correlates with rate of disease progression. J. Immunol. 157:2168–2173 - PubMed
-
- Chung A, Rollman E, Johansson S, Kent SJ, Stratov I. 2008. The utility of ADCC responses in HIV infection. Curr. HIV Res. 6:515–519 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

