Diverse functions of pulmonary collectins in host defense of the lung
- PMID: 22675254
- PMCID: PMC3364019
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/532071
Diverse functions of pulmonary collectins in host defense of the lung
Abstract
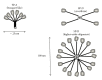
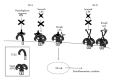
Pulmonary surfactant is a mixture of lipids and proteins that covers alveolar surfaces and keeps alveoli from collapsing. Four specific proteins have been identified in surfactant. Among them, two C-type lectins, surfactant proteins A and D (SP-A and SP-D), are known to be implicated in host defense and regulation of inflammatory responses of the lung. These host defense lectins are structurally characterized by N-terminal collagen-like domains and lectin domains and are called pulmonary collectins. They prevent dissemination of infectious microbes by their biological activities including agglutination and growth inhibition. They also promote clearance of microbes by enhancing phagocytosis in macrophages. In addition, they interact with the other pattern-recognition molecules, including Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and TLR-associated molecules, CD14 and MD-2, and regulate inflammatory responses. Furthermore, recent studies have demonstrated that these collectins modulate functions of neutrophil-derived innate immune molecules by interacting with them. These findings indicate that pulmonary collectins play critical roles in host defense of the lung.
Figures

References
-
- Hoffmann JA, Kafatos FC, Janeway CA, Ezekowitz RAB. Phylogenetic perspectives in innate immunity. Science. 1999;284(5418):1313–1318. - PubMed
-
- King RJ, Clements JA. Surface active materials from dog lung. I. Method of isolation. The American Journal of Physiology. 1972;223(3):707–714. - PubMed
-
- Veldhuizen R, Nag K, Orgeig S, Possmayer F. The role of lipids in pulmonary surfactant. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 1998;1408(2-3):90–108. - PubMed
-
- Kuronuma K, Mitsuzawa H, Takeda K, et al. Anionic pulmonary surfactant phospholipids inhibit inflammatory responses from alveolar macrophages and U937 cells by binding the lipopolysaccharide-interacting proteins CD14 and MD-2. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2009;284(38):25488–25500. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Whitsett JA, Weaver TE. Hydrophobic surfactant proteins in lung function and disease. New England Journal of Medicine. 2002;347(26):2141–2148. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

