Ectopic fat and insulin resistance: pathophysiology and effect of diet and lifestyle interventions
- PMID: 22675355
- PMCID: PMC3366269
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/983814
Ectopic fat and insulin resistance: pathophysiology and effect of diet and lifestyle interventions
Abstract
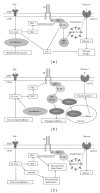
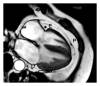
The storage of triglyceride (TG) droplets in nonadipose tissues is called ectopic fat storage. Ectopic fat is associated with insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Not the triglycerides per se but the accumulation of intermediates of lipid metabolism in organs, such as the liver, skeletal muscle, and heart seem to disrupt metabolic processes and impair organ function. We describe the mechanisms of ectopic fat depositions in the liver, skeletal muscle, and in and around the heart and the consequences for each organs function. In addition, we systematically reviewed the literature for the effects of diet-induced weight loss and exercise on ectopic fat depositions.
Figures

References
-
- Obesity and overweight. WHO Report No.: fact sheet no 311, 2012, http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en/index.html.
-
- Pi-Sunyer FX. Medical hazards of obesity. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1993;119(7):655–660. - PubMed
-
- Yanovski SZ. Overweight, obesity, and health risk: National Task Force on the Prevention and Treatment of Obesity. Archives of Internal Medicine. 2000;160(7):898–904. - PubMed
-
- Field AE, Coakley EH, Must A, et al. Impact of overweight on the risk of developing common chronic diseases during a 10-year period. Archives of Internal Medicine. 2001;161(13):1581–1586. - PubMed
-
- Willett WC, Dietz WH, Colditz GA. Guidelines for healthy weight. New England Journal of Medicine. 1999;341(6):427–434. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

