Double digest RADseq: an inexpensive method for de novo SNP discovery and genotyping in model and non-model species
- PMID: 22675423
- PMCID: PMC3365034
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037135
Double digest RADseq: an inexpensive method for de novo SNP discovery and genotyping in model and non-model species
Abstract
The ability to efficiently and accurately determine genotypes is a keystone technology in modern genetics, crucial to studies ranging from clinical diagnostics, to genotype-phenotype association, to reconstruction of ancestry and the detection of selection. To date, high capacity, low cost genotyping has been largely achieved via "SNP chip" microarray-based platforms which require substantial prior knowledge of both genome sequence and variability, and once designed are suitable only for those targeted variable nucleotide sites. This method introduces substantial ascertainment bias and inherently precludes detection of rare or population-specific variants, a major source of information for both population history and genotype-phenotype association. Recent developments in reduced-representation genome sequencing experiments on massively parallel sequencers (commonly referred to as RAD-tag or RADseq) have brought direct sequencing to the problem of population genotyping, but increased cost and procedural and analytical complexity have limited their widespread adoption. Here, we describe a complete laboratory protocol, including a custom combinatorial indexing method, and accompanying software tools to facilitate genotyping across large numbers (hundreds or more) of individuals for a range of markers (hundreds to hundreds of thousands). Our method requires no prior genomic knowledge and achieves per-site and per-individual costs below that of current SNP chip technology, while requiring similar hands-on time investment, comparable amounts of input DNA, and downstream analysis times on the order of hours. Finally, we provide empirical results from the application of this method to both genotyping in a laboratory cross and in wild populations. Because of its flexibility, this modified RADseq approach promises to be applicable to a diversity of biological questions in a wide range of organisms.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

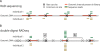
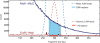
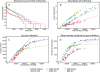
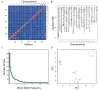
References
-
- Consortium 1000 GP. A map of human genome variation from population-scale sequencing. Nature. 2010;467:1061–1073. doi: 10.1038/nature09534. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Altshuler D, Pollara VJ, Cowles CR, van Etten WJ, Baldwin J, et al. An SNP map of the human genome generated by reduced representation shotgun sequencing. Nature. 2000;407:513–516. doi: 10.1038/35035083. - DOI - PubMed
-
- van Tassell CP, Smith TPL, Matukumalli LK, Taylor JF, Schnabel RD, et al. SNP discovery and allele frequency estimation by deep sequencing of reduced representation libraries. Nature Methods. 2008;5:247–252. doi: 10.1038/NMETH.1185. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gompert Z, Forister ML, Fordyce JA, Nice CC, Williamson RJ, et al. Bayesian analysis of molecular variance in pyrosequences quantifies population genetic structure across the genome of Lycaeides butterflies. Molecular Ecology. 2010;19:2455–2473. doi: 10.1111/j.1365–294X.2010.04666.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

