High quality draft genome sequence of Segniliparus rugosus CDC 945(T)= (ATCC BAA-974(T))
- PMID: 22675588
- PMCID: PMC3368418
- DOI: 10.4056/sigs.2255041
High quality draft genome sequence of Segniliparus rugosus CDC 945(T)= (ATCC BAA-974(T))
Abstract
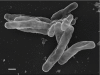
Segniliparus rugosus represents one of two species in the genus Segniliparus, the sole genus in the family Segniliparaceae. A unique and interesting feature of this family is the presence of extremely long carbon-chain length mycolic acids bound in the cell wall. S. rugosus is also a medically important species because it is an opportunistic pathogen associated with mammalian lung disease. This report represents the second species in the genus to have its genome sequenced. The 3,567,567 bp long genome with 3,516 protein-coding and 49 RNA genes is part of the NIH Roadmap for Medical Research, Human Microbiome Project.
Keywords: Human Microbiome Project; Segniliparaceae,genome sequencing.
Figures

References
-
- Butler WR, Floyd MM, Brown JM, Toney SR, Daneshvar MI, Cooksey RC, Carr J, Steigerwalt AG, Charles N. Novel mycolic acid-containing bacteria in the family Segniliparaceae fam. nov., including the genus Segniliparus gen. nov., with descriptions of Segniliparus rotundus sp. nov. and Segniliparus rugosus sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2005; 55:1615-1624 10.1099/ijs.0.63465-0 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

