Protective effects of hyperbaric oxygen and iloprost on ischemia/reperfusion-induced lung injury in a rabbit model
- PMID: 22676276
- PMCID: PMC3406985
- DOI: 10.1186/2047-783X-17-14
Protective effects of hyperbaric oxygen and iloprost on ischemia/reperfusion-induced lung injury in a rabbit model
Abstract
Background: The role of multiorgan damage in the mortality caused by ischemic limb injury is still not clarified. The objective of this study was to examine the potential protective effects of hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) and iloprost (IL) therapy on lung damage induced by limb ischemia/reperfusion injury in a rabbit model, using both biochemical and histopathological aspects.
Methods: Forty New Zealand white rabbits were randomly allocated into one of five study groups: HBO group (single session of HBO treatment); IL group (25 ng/kg/min infusion of IL); HBO + IL group (both HBO and IL); Control group (0.9% saline only); and a sham group. Acute hind limb ischemia-reperfusion was established by clamping the abdominal aorta for 1 h. HBO treatment and IL infusion were administrated during 60 min of ischemia and 60 min of reperfusion period. Blood pH, partial pressure of oxygen, partial pressure of carbon dioxide and levels of bicarbonate, sodium, potassium, creatine kinase, lactate dehydrogenase, and tumor necrosis factor alpha were determined at the end of the reperfusion period. Malondialdehyde was measured in the plasma and lung as an indicator of free radicals. After sacrifice, left lungs were removed and histopathological examination determined the degree of lung injury.
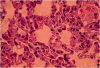
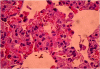
Results: In the control group, blood partial pressure of oxygen and bicarbonate levels were significantly lower and creatine kinase, lactate dehydrogenase, malondialdehyde and tumor necrosis factor-α levels were significantly higher than those of the HBO group, IL group, HBO + IL group and sham group. Similarly, the malondialdehyde levels in the lung tissue and plasma levels were significantly lower in the treatment groups compared with the control group. The extent of lung injury according to the histological findings was significantly higher in the control group.
Conclusions: These results suggest that both HBO and IL therapies and their combination might be effectively used in the prevention of lung injury after ischemia/reperfusion injury of the lower extremities.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of hyperbaric oxygen and iloprost on intestinal ischemia-reperfusion induced acute lung injury.Ann Surg Treat Res. 2019 Jan;96(1):34-40. doi: 10.4174/astr.2019.96.1.34. Epub 2018 Dec 26. Ann Surg Treat Res. 2019. PMID: 30603632 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of combined hyperbaric oxygen and iloprost treatment on the prevention of spinal cord ischaemia-reperfusion injury: an experimental study.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2013 Nov;44(5):e332-40. doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezt398. Epub 2013 Aug 14. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2013. PMID: 23946499
-
Protective effects of levosimendan and iloprost on lung injury induced by limb ischemia-reperfusion: a rabbit model.J Surg Res. 2008 Jun 1;147(1):138-42. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2007.08.002. Epub 2007 Sep 11. J Surg Res. 2008. PMID: 18222476
-
An overview of protective strategies against ischemia/reperfusion injury: The role of hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning.Brain Behav. 2018 Mar 30;8(5):e00959. doi: 10.1002/brb3.959. eCollection 2018 May. Brain Behav. 2018. PMID: 29761012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Survey of Molecular Mechanisms of Hyperbaric Oxygen in Tissue Repair.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 29;22(21):11754. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111754. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769182 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of hyperbaric oxygen and iloprost on intestinal ischemia-reperfusion induced acute lung injury.Ann Surg Treat Res. 2019 Jan;96(1):34-40. doi: 10.4174/astr.2019.96.1.34. Epub 2018 Dec 26. Ann Surg Treat Res. 2019. PMID: 30603632 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen inhibits lipid peroxidation after hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in neonatal rats.Neural Regen Res. 2012 Nov 5;7(31):2424-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2012.31.003. Neural Regen Res. 2012. PMID: 25337092 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of hyperbaric therapy on liver morphofunctional of rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus) after hind limb ischemia-reperfusion injury.Vet World. 2017 Nov;10(11):1337-1342. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2017.1337-1342. Epub 2017 Nov 14. Vet World. 2017. PMID: 29263596 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of hyperbaric oxygen versus iloprost treatment in an experimental rat central retinal artery occlusion model.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2016 Nov;254(11):2209-2215. doi: 10.1007/s00417-016-3444-5. Epub 2016 Aug 2. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2016. PMID: 27480178
-
Therapeutic strategies for chronic wound infection.Chin J Traumatol. 2022 Jan;25(1):11-16. doi: 10.1016/j.cjtee.2021.07.004. Epub 2021 Jul 6. Chin J Traumatol. 2022. PMID: 34315658 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Li C, Jackson RM. Reactive species mechanisms of cellular hypoxia-reoxygenation injury. Am J Physiol. 2002;282:C227–C241. - PubMed
-
- Isbir S, Akgun S, Ak K, Civelek A, Tekeli A, Cobanoglu A. Effect of acute lower limb ischemia/reperfusion injury on the free oxygen radical systems in lung. Turkish J Cardiovasc Surg. 2000;8(2):632–634.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

