Establishment and characterization of a sustained delayed-type hypersensitivity model with arthritic manifestations in C57BL/6J mice
- PMID: 22676339
- PMCID: PMC3446517
- DOI: 10.1186/ar3867
Establishment and characterization of a sustained delayed-type hypersensitivity model with arthritic manifestations in C57BL/6J mice
Abstract
Introduction: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic progressive, inflammatory and destructive autoimmune disease, characterised by synovial joint inflammation and bone erosion. To better understand the pathophysiology and underlying immune mechanisms of RA various models of arthritis have been developed in different inbred strains of mice. Establishment of arthritis models with components of adaptive immunity in the C57BL/6J strain of mice has been difficult, and since most genetically modified mice are commonly bred on this background, there is a need to explore new ways of obtaining robust models of arthritis in this strain. This study was undertaken to establish and characterise a novel murine model of arthritis, the delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH)-arthritis model, and evaluate whether disease can be treated with compounds currently used in the treatment of RA.
Methods: DTH-arthritis was induced by eliciting a classical DTH reaction in one paw with methylated bovine serum albumin (mBSA), with the modification that a cocktail of type II collagen monoclonal antibodies was administered between the immunisation and challenge steps. Involved cell subsets and inflammatory mediators were analysed, and tissue sections evaluated histopathologically. Disease was treated prophylactically and therapeutically with compounds used in the treatment of RA.
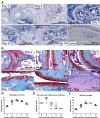
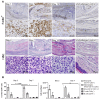
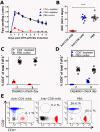
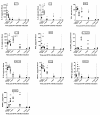
Results: We demonstrate that DTH-arthritis could be induced in C57BL/6 mice with paw swelling lasting for at least 28 days and that disease induction was dependent on CD4+ cells. We show that macrophages and neutrophils were heavily involved in the observed pathology and that a clear profile of inflammatory mediators associated with these cell subsets was induced locally. In addition, inflammatory markers were observed systemically. Furthermore, we demonstrate that disease could be both prevented and treated.
Conclusions: Our findings indicate that DTH-arthritis shares features with both collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) and human RA. DTH-arthritis is dependent on CD4+ cells for induction and can be successfully treated with TNFα-blocking biologics and dexamethasone. On the basis of our findings we believe that the DTH-arthritis model could hold potential in the preclinical screening of novel drugs targeting RA. The model is highly reproducible and has a high incidence rate with synchronised onset and progression, which strengthens its potential.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pharmacological Value of Murine Delayed-type Hypersensitivity Arthritis: A Robust Mouse Model of Rheumatoid Arthritis in C57BL/6 Mice.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2017 Feb;120(2):108-114. doi: 10.1111/bcpt.12657. Epub 2016 Nov 24. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 27553641 Review.
-
Treatment with anti-C5aR mAb leads to early-onset clinical and mechanistic effects in the murine delayed-type hypersensitivity arthritis model.Autoimmunity. 2015;48(7):460-70. doi: 10.3109/08916934.2015.1031888. Epub 2015 Apr 27. Autoimmunity. 2015. PMID: 25915570
-
Administration of anti-type II collagen antibody sustains footpad swelling of mice caused by a delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction and induces severe arthritis.Clin Exp Immunol. 2007 May;148(2):360-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2007.03354.x. Epub 2007 Mar 5. Clin Exp Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17335554 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of a novel and spontaneous mouse model of inflammatory arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2011 Jul 12;13(4):R114. doi: 10.1186/ar3399. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011. PMID: 21749708 Free PMC article.
-
Collagen induced arthritis: an experimental model for rheumatoid arthritis with involvement of both DTH and immune complex mediated mechanisms.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1989 Sep-Oct;7 Suppl 3:S51-5. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1989. PMID: 2691160 Review.
Cited by
-
The Urokinase Plasminogen Activation System in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Pathophysiological Roles and Prospective Therapeutic Targets.Curr Drug Targets. 2019;20(9):970-981. doi: 10.2174/1389450120666181204164140. Curr Drug Targets. 2019. PMID: 30516104 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor cell MT1-MMP is dispensable for osteosarcoma tumor growth, bone degradation and lung metastasis.Sci Rep. 2020 Nov 5;10(1):19138. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-75995-6. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33154487 Free PMC article.
-
Sesquiterpene lactones-enriched fractions from Xanthium mongolicum Kitag alleviate RA by regulating M1 macrophage polarization via NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jan 26;14:1104153. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1104153. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36778009 Free PMC article.
-
Activated, Pro-Inflammatory Th1, Th17, and Memory CD4+ T Cells and B Cells Are Involved in Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity Arthritis (DTHA) Inflammation and Paw Swelling in Mice.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 2;12:689057. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.689057. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34408746 Free PMC article.
-
Potential effects of shift work on skin autoimmune diseases.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 14;13:1000951. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1000951. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36865523 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kollias G, Papadaki P, Apparailly F, Vervoordeldonk MJ, Holmdahl R, Baumans V, Desaintes C, Di Santo J, Distler J, Garside P, Hegen M, Huizinga TW, Jüngel A, Klareskog L, McInnes I, Ragoussis I, Schett G, Hart B, Tak PP, Toes R, van den Berg W, Wurst W, Gay S. Animal models for arthritis: innovative tools for prevention and treatment. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70:1357–1362. doi: 10.1136/ard.2010.148551. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

