Integration of maternal genome into the neonate genome through breast milk mRNA transcripts and reverse transcriptase
- PMID: 22676860
- PMCID: PMC3413567
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-4682-9-20
Integration of maternal genome into the neonate genome through breast milk mRNA transcripts and reverse transcriptase
Abstract
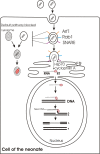
Human milk samples contain microvesicles similar to the retroviruses. These microvesicles contain mRNA transcripts and possess reverse transcriptase activity. They contain about 14,000 transcripts representing the milk transcriptome. Microvesicles are also enriched with proteins related to "caveolar-mediated endocytosis signaling" pathway. It has recently been reported that microvesicles could be transferred to other cells by endocytosis and their RNA content can be translated and be functional in their new location. A significant percentage of the mammalian genome appears to be the product of reverse transcription, containing sequences whose characteristics point to RNA as a template precursor. These are mobile elements that move by way of transposition and are called retrotransposons. We thought that retrotransposons may stem from about 14,000 transcriptome of breast milk microvesicles, and reviewed the literature.The enhanced acceptance of maternal allografts in children who were breast-fed and tolerance to the maternal MHC antigens after breastfeeding may stem from RNAs of the breast milk microvesicles that can be taken up by the breastfed infant and receiving maternal genomic information. We conclude that milk microvesicles may transfer genetic signals from mother to neonate during breastfeeding. Moreover, transfer of wild type RNA from a healthy wet-nurse to the suckling neonate through the milk microvesicles and its subsequent reverse transcription and integration into the neonate genome could result in permanent correction of the clinical manifestations in genetic diseases.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Isolation of bovine milk-derived microvesicles carrying mRNAs and microRNAs.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010 May 28;396(2):528-33. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.04.135. Epub 2010 Apr 29. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010. PMID: 20434431
-
Tumour microvesicles contain retrotransposon elements and amplified oncogene sequences.Nat Commun. 2011 Feb 1;2:180. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1180. Nat Commun. 2011. PMID: 21285958 Free PMC article.
-
[Retroviruses-derived sequences in the human genome. Human endogenous retroviruses (HERVs)].Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2006;60:637-52. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2006. PMID: 17199106 Review. Polish.
-
Breast Milk and Breastfeeding of Infants Born to SARS-CoV-2 Positive Mothers: A Prospective Observational Cohort Study.Am J Perinatol. 2021 Sep;38(11):1209-1216. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1731451. Epub 2021 Jun 28. Am J Perinatol. 2021. PMID: 34182576
-
The effect of medications on the lactating mother and her infant.Clin Obstet Gynecol. 1980 Dec;23(4):1073-80. doi: 10.1097/00003081-198012000-00010. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 1980. PMID: 6160936 Review.
Cited by
-
Milk's Role as an Epigenetic Regulator in Health and Disease.Diseases. 2017 Mar 15;5(1):12. doi: 10.3390/diseases5010012. Diseases. 2017. PMID: 28933365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Milk: an epigenetic amplifier of FTO-mediated transcription? Implications for Western diseases.J Transl Med. 2015 Dec 21;13:385. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0746-z. J Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 26691922 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of extracellular RNA-carrying vesicles in cell differentiation and reprogramming.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015 Sep 3;6:153. doi: 10.1186/s13287-015-0150-x. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 26334526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Orally Administered Exosomes Suppress Mouse Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity by Delivering miRNA-150 to Antigen-Primed Macrophage APC Targeted by Exosome-Surface Anti-Peptide Antibody Light Chains.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 2;21(15):5540. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155540. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32748889 Free PMC article.
-
Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity Underlying Casein Allergy Is Suppressed by Extracellular Vesicles Carrying miRNA-150.Nutrients. 2019 Apr 23;11(4):907. doi: 10.3390/nu11040907. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31018604 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Irmak MK, Oztas Y, Oztas E. RNA-based gene delivery system hidden in breast milk microvesicles. J Exp Integr Med. 2012;2:125–136.
-
- Gallo RC. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase in viruses and cells: Views on the current state. Blood. 1972;39:117–137. - PubMed
-
- Schlom J, Spiegelman S, Moore DH. Reverse transcriptase and high molecular weight RNA in particles from mouse and human milk. J Nat Cancer Inst. 1972;48:1197–1203. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

