Involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in expression of the water channel protein aquaporin-4 after ischemia in rat cortical astrocytes
- PMID: 22676888
- PMCID: PMC3433694
- DOI: 10.1089/neu.2012.2430
Involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in expression of the water channel protein aquaporin-4 after ischemia in rat cortical astrocytes
Abstract
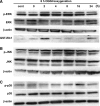
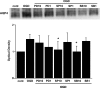
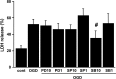
Brain edema after ischemic brain injury is a key determinant of morbidity and mortality. Aquaporin-4 (AQP4) plays an important role in water transport in the central nervous system and is highly expressed in brain astrocytes. However, the AQP4 regulatory mechanisms are poorly understood. In this study, we investigated whether mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), which are involved in changes in osmolality, might mediate AQP4 expression in models of rat cortical astrocytes after ischemia. Increased levels of AQP4 in primary cultured astrocytes subjected to oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD) and 2 h of reoxygenation were observed, after which they immediately decreased at 0 h of reoxygenation. Astrocytes exposed to OGD injury had significantly increased phosphorylation of three kinds of MAPKs. Treatment with SB203580, a selective p38 MAPK inhibitor, or SP600125, a selective c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitor, significantly attenuated the return of AQP4 to its normal level, and SB203580, but not SP600125, significantly decreased cell death. In an in vivo study, AQP4 expression was upregulated 1-3 days after reperfusion, which was consistent with the time course of p38 phosphorylation and activation, and decreased by the p38 inhibition after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO). These results suggest that p38 MAPK may regulate AQP4 expression in cortical astrocytes after ischemic injury.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Propofol inhibits aquaporin 4 expression through a protein kinase C-dependent pathway in an astrocyte model of cerebral ischemia/reoxygenation.Anesth Analg. 2009 Nov;109(5):1493-9. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e3181b893f3. Anesth Analg. 2009. PMID: 19843787
-
[Role of P38 signaling pathway in neonatal rat astrocyte swelling and aquaporin-4 expression after oxygen-glucose deprivation and recovery].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2012 Feb;32(2):141-5. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2012. PMID: 22381744 Chinese.
-
Involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in ferrous iron-induced aquaporin-4 expression in cultured astrocytes.Neurotoxicology. 2019 Jul;73:142-149. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2019.03.006. Epub 2019 Mar 23. Neurotoxicology. 2019. PMID: 30914277
-
Remote ischemic post-conditioning improves neurological function by AQP4 down-regulation in astrocytes.Behav Brain Res. 2015 Aug 1;289:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2015.04.024. Epub 2015 Apr 21. Behav Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25907740 Review.
-
Failure and function of intracellular pH regulation in acute hypoxic-ischemic injury of astrocytes.Glia. 2005 Jun;50(4):398-406. doi: 10.1002/glia.20141. Glia. 2005. PMID: 15846798 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation and Function of AQP4 in the Central Nervous System.Neurochem Res. 2015 Dec;40(12):2615-27. doi: 10.1007/s11064-015-1519-z. Epub 2015 Jan 29. Neurochem Res. 2015. PMID: 25630715 Review.
-
Involvement of JNK/NFκB Signaling Pathways in the Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Modulation of Aquaglyceroporin Expression in 3T3-L1 Cells Differentiated into Adipocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Oct 18;17(10):1742. doi: 10.3390/ijms17101742. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27763558 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective effects of erythropoietin against hypoxic injury via modulation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway and apoptosis.Korean J Pediatr. 2017 Jun;60(6):181-188. doi: 10.3345/kjp.2017.60.6.181. Epub 2017 Jun 22. Korean J Pediatr. 2017. PMID: 28690645 Free PMC article.
-
miR‑29a ameliorates ischemic injury of astrocytes in vitro by targeting the water channel protein aquaporin 4.Oncol Rep. 2019 Mar;41(3):1707-1717. doi: 10.3892/or.2019.6961. Epub 2019 Jan 9. Oncol Rep. 2019. PMID: 30628716 Free PMC article.
-
Obstructive sleep apnea affects cognition: dual effects of intermittent hypoxia on neurons.Sleep Breath. 2024 Jun;28(3):1051-1065. doi: 10.1007/s11325-024-03001-8. Epub 2024 Feb 3. Sleep Breath. 2024. PMID: 38308748 Review.
References
-
- Arima H. Yamamoto N. Sobue K. Umenishi F. Tada T. Katsuya H. Asai K. Hyperosmolar mannitol stimulates expression of aquaporins 4 and 9 through a p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent pathway in rat astrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:44525–44534. - PubMed
-
- Barone F.C. Irving E.A. Ray A.M. Lee J.C. Kassis S. Kumar S. Badger A.M. Legos J.J. Erhardt J.A. Ohlstein E.H. Hunter A.J. Harrison D.C. Philpott K. Smith B.R. Adams J.L. Parsons A.A. Inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase provides neuroprotection in cerebral focal ischemia. Med. Res. Rev. 2001;21:129–145. - PubMed
-
- Fazzina G. Amorini A.M. Marmarou C.R. Fukui S. Okuno K. Dunbar J.G. Glisson R. Marmarou A. Kleindienst A. The protein kinase C activator phorbol myristate acetate decreases brain edema by aquaporin 4 downregulation after middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat. J. Neurotrauma. 2010;27:453–461. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

