Preclinical activity of a novel CRM1 inhibitor in acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 22677130
- PMCID: PMC3433086
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2012-04-423160
Preclinical activity of a novel CRM1 inhibitor in acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
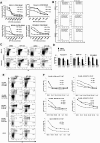
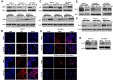
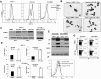
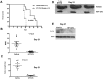
Chromosome maintenance protein 1 (CRM1) is a nuclear export receptor involved in the active transport of tumor suppressors (e.g., p53 and nucleophosmin) whose function is altered in cancer because of increased expression and overactive transport. Blocking CRM1-mediated nuclear export of such proteins is a novel therapeutic strategy to restore tumor suppressor function. Orally bioavailable selective inhibitors of nuclear export (SINE) that irreversibly bind to CRM1 and block the function of this protein have been recently developed. Here we investigated the antileukemic activity of KPT-SINE (KPT-185 and KPT-276) in vitro and in vivo in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). KPT-185 displayed potent antiproliferative properties at submicromolar concentrations (IC50 values; 100-500 nM), induced apoptosis (average 5-fold increase), cell-cycle arrest, and myeloid differentiation in AML cell lines and patient blasts. A strong down-regulation of the oncogene FLT3 after KPT treatment in both FLT3-ITD and wild-type cell lines was observed. Finally, using the FLT3-ITD-positive MV4-11 xenograft murine model, we show that treatment of mice with oral KPT-276 (analog of KPT-185 for in vivo studies) significantly prolongs survival of leukemic mice (P < .01). In summary, KPT-SINE are highly potent in vitro and in vivo in AML. The preclinical results reported here support clinical trials of KPT-SINE in AML.
Figures
Comment in
-
A drug that stops traffic at the nuclear border.Blood. 2012 Aug 30;120(9):1759-60. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-07-439166. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22936736 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
KPT-330 inhibitor of XPO1-mediated nuclear export has anti-proliferative activity in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2014 Sep;74(3):487-95. doi: 10.1007/s00280-014-2495-8. Epub 2014 Jul 17. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25030088 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical antitumor efficacy of selective exportin 1 inhibitors in glioblastoma.Neuro Oncol. 2015 May;17(5):697-707. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nou303. Epub 2014 Nov 2. Neuro Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25366336 Free PMC article.
-
Antitumor effects of a novel chromosome region maintenance 1 (CRM1) inhibitor on non-small cell lung cancer cells in vitro and in mouse tumor xenografts.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 4;9(3):e89848. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089848. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24595136 Free PMC article.
-
Expression, function, and targeting of the nuclear exporter chromosome region maintenance 1 (CRM1) protein.Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Sep;153:25-35. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2015.06.001. Epub 2015 Jun 3. Pharmacol Ther. 2015. PMID: 26048327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of CRM1-dependent nuclear export sensitizes malignant cells to cytotoxic and targeted agents.Semin Cancer Biol. 2014 Aug;27:62-73. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2014.03.001. Epub 2014 Mar 12. Semin Cancer Biol. 2014. PMID: 24631834 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Small Molecule Inhibitors of CRM1.Front Pharmacol. 2020 May 7;11:625. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00625. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32574233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interferon-γ Promotes Antibody-mediated Fratricide of Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells.J Biol Chem. 2016 Dec 2;291(49):25656-25666. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.753145. Epub 2016 Oct 25. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27780867 Free PMC article.
-
The use of molecular genetics to refine prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia.Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2014 Jun;9(2):148-57. doi: 10.1007/s11899-014-0208-3. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2014. PMID: 24659319 Review.
-
A phase I study of selinexor in combination with high-dose cytarabine and mitoxantrone for remission induction in patients with acute myeloid leukemia.J Hematol Oncol. 2018 Jan 5;11(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s13045-017-0550-8. J Hematol Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29304833 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Snail nuclear transport: the gateways regulating epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition?Semin Cancer Biol. 2014 Aug;27:39-45. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2014.06.003. Epub 2014 Jun 17. Semin Cancer Biol. 2014. PMID: 24954011 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bednenko J, Cingolani G, Gerace L. Nucleocytoplasmic transport: navigating the channel. Traffic. 2003;4(3):127–135. - PubMed
-
- Hutten S, Kehlenbach RH. CRM1-mediated nuclear export: to the pore and beyond. Trends Cell Biol. 2007;17(4):193–201. - PubMed
-
- Turner JG, Sullivan DM. CRM1-mediated nuclear export of proteins and drug resistance in cancer. Curr Med Chem. 2008;15(26):2648–2655. - PubMed
-
- Fukuda M, Asano S, Nakamura T, et al. CRM1 is responsible for intracellular transport mediated by the nuclear export signal. Nature. 1997;390(6657):308–311. - PubMed
-
- Ossareh-Nazari B, Bachelerie F, Dargemont C. Evidence for a role of CRM1 in signal-mediated nuclear protein export. Science. 1997;278(5335):141–144. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

