Preclinical activity of a novel CRM1 inhibitor in acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 22677130
- PMCID: PMC3433086
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2012-04-423160
Preclinical activity of a novel CRM1 inhibitor in acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
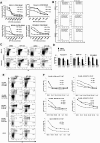
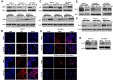
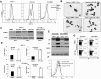
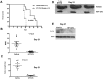
Chromosome maintenance protein 1 (CRM1) is a nuclear export receptor involved in the active transport of tumor suppressors (e.g., p53 and nucleophosmin) whose function is altered in cancer because of increased expression and overactive transport. Blocking CRM1-mediated nuclear export of such proteins is a novel therapeutic strategy to restore tumor suppressor function. Orally bioavailable selective inhibitors of nuclear export (SINE) that irreversibly bind to CRM1 and block the function of this protein have been recently developed. Here we investigated the antileukemic activity of KPT-SINE (KPT-185 and KPT-276) in vitro and in vivo in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). KPT-185 displayed potent antiproliferative properties at submicromolar concentrations (IC50 values; 100-500 nM), induced apoptosis (average 5-fold increase), cell-cycle arrest, and myeloid differentiation in AML cell lines and patient blasts. A strong down-regulation of the oncogene FLT3 after KPT treatment in both FLT3-ITD and wild-type cell lines was observed. Finally, using the FLT3-ITD-positive MV4-11 xenograft murine model, we show that treatment of mice with oral KPT-276 (analog of KPT-185 for in vivo studies) significantly prolongs survival of leukemic mice (P < .01). In summary, KPT-SINE are highly potent in vitro and in vivo in AML. The preclinical results reported here support clinical trials of KPT-SINE in AML.
Figures
Comment in
-
A drug that stops traffic at the nuclear border.Blood. 2012 Aug 30;120(9):1759-60. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-07-439166. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22936736 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bednenko J, Cingolani G, Gerace L. Nucleocytoplasmic transport: navigating the channel. Traffic. 2003;4(3):127–135. - PubMed
-
- Hutten S, Kehlenbach RH. CRM1-mediated nuclear export: to the pore and beyond. Trends Cell Biol. 2007;17(4):193–201. - PubMed
-
- Turner JG, Sullivan DM. CRM1-mediated nuclear export of proteins and drug resistance in cancer. Curr Med Chem. 2008;15(26):2648–2655. - PubMed
-
- Fukuda M, Asano S, Nakamura T, et al. CRM1 is responsible for intracellular transport mediated by the nuclear export signal. Nature. 1997;390(6657):308–311. - PubMed
-
- Ossareh-Nazari B, Bachelerie F, Dargemont C. Evidence for a role of CRM1 in signal-mediated nuclear protein export. Science. 1997;278(5335):141–144. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

