Increasing phosphatidylinositol (4,5) bisphosphate biosynthesis affects plant nuclear lipids and nuclear functions
- PMID: 22677448
- PMCID: PMC3601448
- DOI: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2012.05.011
Increasing phosphatidylinositol (4,5) bisphosphate biosynthesis affects plant nuclear lipids and nuclear functions
Abstract
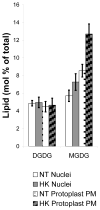
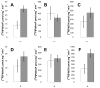
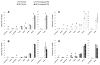
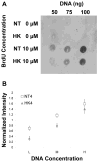
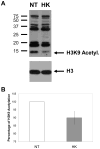
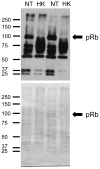
In order to characterize the effects of increasing phosphatidylinositol(4,5)bisphosphate (PtdIns(4,5)P(2)) on nuclear function, we expressed the human phosphatidylinositol (4)-phosphate 5-kinase (HsPIP5K) 1α in Nicotiana tabacum (NT) cells. The HsPIP5K-expressing (HK) cells had altered nuclear lipids and nuclear functions. HK cell nuclei had 2-fold increased PIP5K activity and increased steady state PtdIns(4,5)P(2). HK nuclear lipid classes showed significant changes compared to NT (wild type) nuclear lipid classes including increased phosphatidylserine (PtdSer) and phosphatidylcholine (PtdCho) and decreased lysolipids. Lipids isolated from protoplast plasma membranes (PM) were also analyzed and compared with nuclear lipids. The lipid profiles revealed similarities and differences in the plasma membrane and nuclei from the NT and transgenic HK cell lines. A notable characteristic of nuclear lipids from both cell types is that PtdIns accounts for a higher mol% of total lipids compared to that of the protoplast PM lipids. The lipid molecular species composition of each lipid class was also analyzed for nuclei and protoplast PM samples. To determine whether expression of HsPIP5K1α affected plant nuclear functions, we compared DNA replication, histone 3 lysine 9 acetylation (H3K9ac) and phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma protein (pRb) in NT and HK cells. The HK cells had a measurable decrease in DNA replication, histone H3K9 acetylation and pRB phosphorylation.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Melser S, Molino D, Batailler B, Peypelut M, Laloi M, Wattelet-Boyer V, et al. Links between lipid homeostasis, organelle morphodynamics and protein trafficking in eukaryotic and plant secretory pathways. Plant Cell Reports. 2011;30:177–193. - PubMed
-
- Szumlanski AL, Nielsen E. Phosphatidylinositol 4-Phosphate is Required for Tip Growth in Arabidopsis thaliana. In: Munnik T, editor. Lipid Signaling in Plants. Springer Berlin Heidelberg; Berlin, Heidelberg: 2010. pp. 65–77.
-
- Thole JM, Nielsen E. Phosphoinositides in plants: novel functions in membrane trafficking. Current Opinion in Plant Biology. 2008;11:620–631. - PubMed
-
- Albi E, Viola Magni MP. The role of intranuclear lipids. Biol Cell. 2004;96:657–667. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

