The pharmacological profile of ELIC, a prokaryotic GABA-gated receptor
- PMID: 22677470
- PMCID: PMC3430861
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.05.027
The pharmacological profile of ELIC, a prokaryotic GABA-gated receptor
Abstract
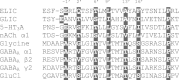
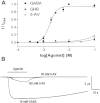
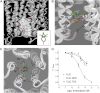
The Erwinia ligand-gated ion channel (ELIC) is a bacterial homologue of vertebrate Cys-loop ligand-gated ion channels. It is activated by GABA, and this property, combined with its structural similarity to GABA(A) and other Cys-loop receptors, makes it potentially an excellent model to probe their structure and function. Here we characterise the pharmacological profile of ELIC, examining the effects of compounds that could activate or inhibit the receptor. We confirm that a range of amino acids and classic GABA(A) receptor agonists do not elicit responses in ELIC, and we show the receptor can be at least partially activated by 5-aminovaleric acid and γ-hydroxybutyric acid, which are weak agonists. A range of GABA(A) receptor non-competitive antagonists inhibit GABA-elicited ELIC responses including α-endosulfan (IC₅₀ = 17 μM), dieldrin (IC₅₀ = 66 μM), and picrotoxinin (IC₅₀ = 96 μM) which were the most potent. Docking suggested possible interactions at the 2' and 6' pore-lining residues, and mutagenesis of these residues supports this hypothesis for α-endosulfan. A selection of compounds that act at Cys-loop and other receptors also showed some efficacy at blocking ELIC responses, but most were of low potency (IC₅₀ > 100 μM). Overall our data show that a number of compounds can inhibit ELIC, but it has limited pharmacological similarity to GLIC and to Cys-loop receptors.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Phenylalanine in the pore of the Erwinia ligand-gated ion channel modulates picrotoxinin potency but not receptor function.Biochemistry. 2014 Oct 7;53(39):6183-8. doi: 10.1021/bi5008035. Epub 2014 Sep 19. Biochemistry. 2014. PMID: 25238029 Free PMC article.
-
Probing Proline Residues in the Prokaryotic Ligand-Gated Ion Channel, ELIC.Biochemistry. 2018 Jul 10;57(27):4036-4043. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.8b00379. Epub 2018 Jun 21. Biochemistry. 2018. PMID: 29927250
-
Allosteric binding site in a Cys-loop receptor ligand-binding domain unveiled in the crystal structure of ELIC in complex with chlorpromazine.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Oct 25;113(43):E6696-E6703. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1603101113. Epub 2016 Oct 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27791038 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into Cys-loop receptor function and ligand recognition.Biochem Pharmacol. 2013 Oct 15;86(8):1042-53. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2013.07.001. Epub 2013 Jul 10. Biochem Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23850718 Review.
-
Atomic structure and dynamics of pentameric ligand-gated ion channels: new insight from bacterial homologues.J Physiol. 2010 Feb 15;588(Pt 4):565-72. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.183160. Epub 2009 Dec 7. J Physiol. 2010. PMID: 19995852 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Macroscopic kinetics of pentameric ligand gated ion channels: comparisons between two prokaryotic channels and one eukaryotic channel.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 19;8(11):e80322. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080322. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24260369 Free PMC article.
-
A chimeric prokaryotic-eukaryotic pentameric ligand gated ion channel reveals interactions between the extracellular and transmembrane domains shape neurosteroid modulation.Neuropharmacology. 2017 Oct;125:343-352. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.08.007. Epub 2017 Aug 10. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 28803966 Free PMC article.
-
Multisite binding of a general anesthetic to the prokaryotic pentameric Erwinia chrysanthemi ligand-gated ion channel (ELIC).J Biol Chem. 2013 Mar 22;288(12):8355-8364. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.424507. Epub 2013 Jan 30. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23364792 Free PMC article.
-
The atypical cation-conduction and gating properties of ELIC underscore the marked functional versatility of the pentameric ligand-gated ion-channel fold.J Gen Physiol. 2015 Jul;146(1):15-36. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201411333. Epub 2015 Jun 15. J Gen Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26078054 Free PMC article.
-
ELIC-α7 Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (α7nAChR) chimeras reveal a prominent role of the extracellular-transmembrane domain interface in allosteric modulation.J Biol Chem. 2014 May 16;289(20):13851-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.524611. Epub 2014 Apr 2. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24695730 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abalis I.M., Eldefrawi A.T., Eldefrawi M.E. High affinity stereospecific binding of cyclodiene insecticides and γ-hexachlorohexane to γ-aminobutyric acid receptors. Pest. Biochem. Physiol. 1985;24:95–102.
-
- Bocquet N., Nury H., Baaden M., Le Poupon C., Changeux J.P., Delarue M., Corringer P.J. X-ray structure of a pentameric ligand-gated ion channel in an apparently open conformation. Nature. 2009;457:111–114. - PubMed
-
- Brejc K., van Dijk W.J., Klaassen R.V., Schuurmans M., van Der Oost J., Smit A.B., Sixma T.K. Crystal structure of an ACh-binding protein reveals the ligand-binding domain of nicotinic receptors. Nature. 2001;411:269–276. - PubMed
-
- Buisson B., Bertrand D. Open-channel blockers at the human α4β2 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 1998;53:555–563. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

