AKAP79 modulation of L-type channels involves disruption of intramolecular interactions in the CaV1.2 subunit
- PMID: 22677788
- PMCID: PMC3431589
- DOI: 10.4161/chan.20865
AKAP79 modulation of L-type channels involves disruption of intramolecular interactions in the CaV1.2 subunit
Abstract
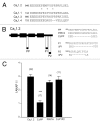
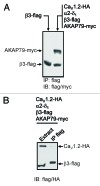
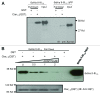
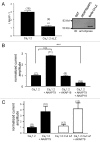
L-type voltage gated calcium channels (VGCCs) interact with a variety of proteins that modulate both their function and localization. A-Kinase Anchoring Proteins (AKAPs) facilitate L-type calcium channel phosphorylation through β adrenergic stimulation. Our previous work indicated a role of neuronal AKAP79/150 in the membrane targeting of Ca(V)1.2 L-type calcium channels, which involved a proline rich domain (PRD) in the intracellular II-III loop of the channel.(1) Here, we show that mutation of proline 857 to alanine (P857A) into the PRD does not disrupt the AKAP79-induced increase in Ca(v)1.2 membrane expression. Furthermore, deletion of two other PRDs into the carboxy terminal domain of Ca(V)1.2 did not alter the targeting role of AKAP79. In contrast, the distal carboxy terminus region of the channel directly interacts with AKAP79. This protein-protein interaction competes with a direct association of the channel II-III linker on the carboxy terminal tail and modulates membrane targeting of Ca(V)1.2. Thus, our results suggest that the effects of AKAP79 occur through relief of an autoinhibitory mechanism mediated by intramolecular interactions of Ca(v)1.2 intracellular regions.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Stable membrane expression of postsynaptic CaV1.2 calcium channel clusters is independent of interactions with AKAP79/150 and PDZ proteins.J Neurosci. 2008 Dec 17;28(51):13845-55. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3213-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 19091974 Free PMC article.
-
Localized calcineurin confers Ca2+-dependent inactivation on neuronal L-type Ca2+ channels.J Neurosci. 2012 Oct 31;32(44):15328-37. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2302-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23115171 Free PMC article.
-
Trafficking of L-type calcium channels mediated by the postsynaptic scaffolding protein AKAP79.J Biol Chem. 2002 Sep 13;277(37):33598-603. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M202476200. Epub 2002 Jul 11. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12114507
-
A macromolecular trafficking complex composed of β₂-adrenergic receptors, A-Kinase Anchoring Proteins and L-type calcium channels.J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2013 Jun;33(3):172-6. doi: 10.3109/10799893.2013.782219. Epub 2013 Apr 4. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2013. PMID: 23557075 Review.
-
Mechanisms and dynamics of AKAP79/150-orchestrated multi-protein signalling complexes in brain and peripheral nerve.J Physiol. 2016 Jan 1;594(1):31-7. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2014.287698. Epub 2015 Mar 11. J Physiol. 2016. PMID: 25653013 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
C-terminal modulatory domain controls coupling of voltage-sensing to pore opening in Cav1.3 L-type Ca(2+) channels.Biophys J. 2014 Apr 1;106(7):1467-75. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2014.02.017. Biophys J. 2014. PMID: 24703308 Free PMC article.
-
L-type Ca2+ channels in heart and brain.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Membr Transp Signal. 2014 Mar 1;3(2):15-38. doi: 10.1002/wmts.102. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Membr Transp Signal. 2014. PMID: 24683526 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenicity of de novo CACNA1D Ca2+ channel variants predicted from sequence co-variation.Eur J Hum Genet. 2024 Sep;32(9):1065-1073. doi: 10.1038/s41431-024-01594-y. Epub 2024 Mar 29. Eur J Hum Genet. 2024. PMID: 38553610 Free PMC article.
-
L-type Ca2+ channel function during Timothy syndrome.Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2012 Apr;22(3):72-6. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2012.06.015. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2012. PMID: 22999068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapid Turnover of the Cardiac L-Type CaV1.2 Channel by Endocytic Recycling Regulates Its Cell Surface Availability.iScience. 2018 Sep 28;7:1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2018.08.012. Epub 2018 Aug 16. iScience. 2018. PMID: 30267672 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
