Kinetic analysis reveals successive steps leading to miRNA-mediated silencing in mammalian cells
- PMID: 22677978
- PMCID: PMC3410385
- DOI: 10.1038/embor.2012.82
Kinetic analysis reveals successive steps leading to miRNA-mediated silencing in mammalian cells
Abstract
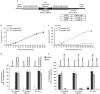
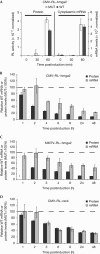
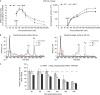
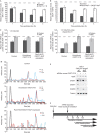
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) regulate most cellular functions, acting by posttranscriptionally repressing numerous eukaryotic mRNAs. They lead to translational repression, deadenylation and degradation of their target mRNAs. Yet, the relative contributions of these effects are controversial and little is known about the sequence of events occurring during the miRNA-induced response. Using stable human cell lines expressing inducible reporters, we found that translational repression is the dominant effect of miRNAs on newly synthesized targets. This step is followed by mRNA deadenylation and decay, which is the dominant effect at steady state. Our findings have important implications for understanding the mechanism of silencing and reconcile seemingly contradictory data.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bushati N, Cohen SM (2007) microRNA functions. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 23: 175–205 - PubMed
-
- Fabian MR, Sonenberg N, Filipowicz W (2010) Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu Rev Biochem 79: 351–379 - PubMed
-
- Braun JE, Huntzinger E, Fauser M, Izaurralde E (2011) GW182 Proteins directly recruit cytoplasmic deadenylase complexes to miRNA targets. Mol Cell 44: 120–133 - PubMed
-
- Fabian MR et al. (2011) miRNA-mediated deadenylation is orchestrated by GW182 through two conserved motifs that interact with CCR4-NOT. Nat Struct Mol Biol 18: 1211–1217 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

