A novel microtubule-modulating agent EM011 inhibits angiogenesis by repressing the HIF-1α axis and disrupting cell polarity and migration
- PMID: 22678119
- PMCID: PMC3514903
- DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgs200
A novel microtubule-modulating agent EM011 inhibits angiogenesis by repressing the HIF-1α axis and disrupting cell polarity and migration
Abstract
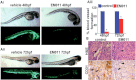
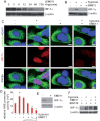
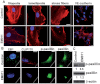
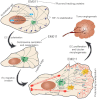
Endothelial tubular morphogenesis relies on an exquisite interplay of microtubule dynamics and actin remodeling to propel directed cell migration. Recently, the dynamicity and integrity of microtubules have been implicated in the trafficking and efficient translation of the mRNA for HIF-1α (hypoxia-inducible factor), the master regulator of tumor angiogenesis. Thus, microtubule-disrupting agents that perturb the HIF-1α axis and neovascularization cascade are attractive anticancer drug candidates. Here we show that EM011 (9-bromonoscapine), a microtubule-modulating agent, inhibits a spectrum of angiogenic events by interfering with endothelial cell invasion, migration and proliferation. Employing green-fluorescent transgenic zebrafish, we found that EM011 not only inhibited vasculogenesis but also disrupted preexisting vasculature. Mechanistically, EM011 caused proteasome-dependent, VHL-independent HIF-1α degradation and repressed expression of HIF-1α downstream targets, namely VEGF and survivin. Furthermore, EM011 inhibited membrane ruffling and impeded formation of filopodia, lamellipodia and stress fibers, which are critical for cell migration. These events were associated with a drug-mediated decrease in activation of Rho GTPases- RhoA, Cdc42 and Rac1, and correlated with a loss in the geometric precision of centrosome reorientation in the direction of movement. This is the first report to describe a previously unrecognized, antiangiogenic property of a noscapinoid, EM011, and provides evidence for novel anticancer strategies recruited by microtubule-modulating drugs.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Modulating the hypoxia-inducible factor signaling pathway as a therapeutic modality to regulate retinal angiogenesis.Exp Eye Res. 2009 Nov;89(5):700-17. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2009.06.013. Epub 2009 Jul 4. Exp Eye Res. 2009. PMID: 19580810
-
A novel microtubule-modulating noscapinoid triggers apoptosis by inducing spindle multipolarity via centrosome amplification and declustering.Cell Death Differ. 2011 Apr;18(4):632-44. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2010.133. Epub 2010 Nov 5. Cell Death Differ. 2011. PMID: 21052096 Free PMC article.
-
Fasudil-induced hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha degradation disrupts a hypoxia-driven vascular endothelial growth factor autocrine mechanism in endothelial cells.Mol Cancer Ther. 2008 Jun;7(6):1551-61. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-0428. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008. PMID: 18566226
-
A novel inhibitor of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α P3155 also modulates PI3K pathway and inhibits growth of prostate cancer cells.BMC Cancer. 2011 Aug 5;11:338. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-338. BMC Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21819554 Free PMC article.
-
What tangled webs they weave: Rho-GTPase control of angiogenesis.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2007 Aug;64(16):2053-65. doi: 10.1007/s00018-007-7008-z. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2007. PMID: 17530172 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tryptone-stabilized gold nanoparticles induce unipolar clustering of supernumerary centrosomes and G1 arrest in triple-negative breast cancer cells.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 13;9(1):19126. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-55555-3. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31836782 Free PMC article.
-
Zebrafish as a disease model for studying human hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Nov 14;21(42):12042-58. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i42.12042. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26576090 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Endothelial Centrosome: Specific Features and Functional Significance for Endothelial Cell Activity and Barrier Maintenance.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 20;24(20):15392. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015392. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37895072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In-Vitro and Ex-Vivo Investigations of the Microtubule Binding Drug Targetin on Angiogenesis.J Pediatr Oncol. 2013;1:41-47. doi: 10.14205/2309-3021.2013.01.01.6. J Pediatr Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24749126 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of 2-Methoxyestradiol and Sex on Hypoxia-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension and Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1-α.J Am Heart Assoc. 2019 Mar 5;8(5):e011628. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.118.011628. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019. PMID: 30819028 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wittmann T, et al. (2001). Cell motility: can Rho GTPases and microtubules point the way? J. Cell Sci. 114 3795–3803 - PubMed
-
- Lauffenburger D.A., et al. (1996). Cell migration: a physically integrated molecular process Cell 84 359–369 - PubMed
-
- Waterman-Storer C.M., et al. (1999). Positive feedback interactions between microtubule and actin dynamics during cell motility Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 11 61–67 - PubMed
-
- Small J.V., et al. (2003). Microtubules meet substrate adhesions to arrange cell polarity Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 15 40–47 - PubMed
-
- Mabjeesh N.J., et al. (2003). 2ME2 inhibits tumor growth and angiogenesis by disrupting microtubules and dysregulating HIF Cancer Cell 3 363–375 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

