Preclinical evaluation of an MRI-compatible pneumatic robot for angulated needle placement in transperineal prostate interventions
- PMID: 22678723
- PMCID: PMC3692285
- DOI: 10.1007/s11548-012-0750-1
Preclinical evaluation of an MRI-compatible pneumatic robot for angulated needle placement in transperineal prostate interventions
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the targeting accuracy of a small profile MRI-compatible pneumatic robot for needle placement that can angulate a needle insertion path into a large accessible target volume.
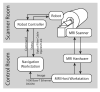
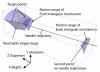
Methods: We extended our MRI-compatible pneumatic robot for needle placement to utilize its four degrees-of-freedom (4-DOF) mechanism with two parallel triangular structures and support transperineal prostate biopsies in a closed-bore magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanner. The robot is designed to guide a needle toward a lesion so that a radiologist can manually insert it in the bore. The robot is integrated with navigation software that allows an operator to plan angulated needle insertion by selecting a target and an entry point. The targeting error was evaluated while the angle between the needle insertion path and the static magnetic field was between -5.7° and 5.7° horizontally and between -5.7° and 4.3° vertically in the MRI scanner after sterilizing and draping the device.
Results: The robot positioned the needle for angulated insertion as specified on the navigation software with overall targeting error of 0.8 ± 0.5mm along the horizontal axis and 0.8 ± 0.8mm along the vertical axis. The two-dimensional root-mean-square targeting error on the axial slices as containing the targets was 1.4mm.
Conclusions: Our preclinical evaluation demonstrated that the MRI-compatible pneumatic robot for needle placement with the capability to angulate the needle insertion path provides targeting accuracy feasible for clinical MRI-guided prostate interventions. The clinical feasibility has to be established in a clinical study.
Figures

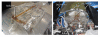


Similar articles
-
In vivo evaluation of angulated needle-guide template for MRI-guided transperineal prostate biopsy.Med Phys. 2021 May;48(5):2553-2565. doi: 10.1002/mp.14816. Epub 2021 Mar 24. Med Phys. 2021. PMID: 33651407 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of robot-assisted MRI-guided prostate biopsy: needle path analysis during clinical trials.Phys Med Biol. 2018 Oct 16;63(20):20NT02. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/aae214. Phys Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 30226214 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy study of a robotic system for MRI-guided prostate needle placement.Int J Med Robot. 2013 Sep;9(3):305-16. doi: 10.1002/rcs.1440. Epub 2012 Jun 8. Int J Med Robot. 2013. PMID: 22678990 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements in magnetic resonance-guided robotic interventions in the prostate.Top Magn Reson Imaging. 2008 Dec;19(6):297-304. doi: 10.1097/RMR.0b013e3181aa68b8. Top Magn Reson Imaging. 2008. PMID: 19512852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MRI-guided and robotic-assisted prostate biopsy.Curr Opin Urol. 2012 Jul;22(4):316-9. doi: 10.1097/MOU.0b013e328354833c. Curr Opin Urol. 2012. PMID: 22617059 Review.
Cited by
-
State of the Art and Future Opportunities in MRI-Guided Robot-Assisted Surgery and Interventions.Proc IEEE Inst Electr Electron Eng. 2022 Jul;110(7):968-992. doi: 10.1109/jproc.2022.3169146. Epub 2022 May 3. Proc IEEE Inst Electr Electron Eng. 2022. PMID: 35756185 Free PMC article.
-
Design, Additive Manufacture, and Control of a Pneumatic, MR-Compatible Needle Driver.IEEE Trans Robot. 2016 Feb;32(1):138-149. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2015.2504981. Epub 2016 Jan 19. IEEE Trans Robot. 2016. PMID: 31105476 Free PMC article.
-
MRI-Safe Robot for Endorectal Prostate Biopsy.IEEE ASME Trans Mechatron. 2013 Sep 16;19(4):1289-1299. doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2013.2279775. IEEE ASME Trans Mechatron. 2013. PMID: 25378897 Free PMC article.
-
System Integration and Preliminary Clinical Evaluation of a Robotic System for MRI-Guided Transperineal Prostate Biopsy.J Med Robot Res. 2019 Jun;4(2):1950001. doi: 10.1142/S2424905X19500016. Epub 2018 May 15. J Med Robot Res. 2019. PMID: 31485544 Free PMC article.
-
Robot-assisted flexible needle insertion using universal distributional deep reinforcement learning.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2020 Feb;15(2):341-349. doi: 10.1007/s11548-019-02098-7. Epub 2019 Nov 25. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2020. PMID: 31768886
References
-
- Cormack RA, D’Amico AV, Hata N, Silverman S, Weinstein M, Tempany CM. Feasibility of transperineal prostate biopsy under interventional magnetic resonance guidance. Urology. 2000;56(4):663–664. doi:S0090-4295(00)00698-1 [pii] - PubMed
-
- D’Amico AV, Tempany CM, Cormack R, Hata N, Jinzaki M, Tuncali K, Weinstein M, Richie JP. Transperineal magnetic resonance image guided prostate biopsy. J Urol. 2000;164(2):385–387. doi:S0022-5347(05)67366-1 [pii] - PubMed
-
- Menard C, Susil RC, Choyke P, Gustafson GS, Kammerer W, Ning H, Miller RW, Ullman KL, Sears Crouse N, Smith S, Lessard E, Pouliot J, Wright V, McVeigh E, Coleman CN, Camphausen K. MRI-guided HDR prostate brachytherapy in standard 1.5T scanner. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004;59(5):1414–1423. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2004.01.016 S036030160400118X [pii] - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

