Kruppel-like factor 4 contributes to high phosphate-induced phenotypic switching of vascular smooth muscle cells into osteogenic cells
- PMID: 22679022
- PMCID: PMC3406659
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.361360
Kruppel-like factor 4 contributes to high phosphate-induced phenotypic switching of vascular smooth muscle cells into osteogenic cells
Abstract
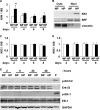
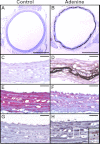
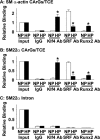
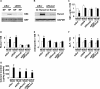
Hyperphosphatemia in chronic kidney disease is highly associated with vascular calcification. Previous studies have shown that high phosphate-induced phenotypic switching of vascular smooth muscle cells (SMCs) into osteogenic cells plays an important role in the calcification process. In the present study, we determined whether Krüppel-like factor 4 (Klf4) and phosphorylated Elk-1, transcriptional repressors of SMC differentiation marker genes activated by intimal atherogenic stimuli, contributed to this process. Rat aortic SMCs were cultured in the medium with normal (0.9 mmol/liter) or high (4.5 mmol/liter) phosphate concentration. Results showed that high phosphate concentration induced SMC calcification. Moreover, high phosphate decreased expression of SMC differentiation marker genes including smooth muscle α-actin and SM22α, whereas it increased expression of osteogenic genes, such as Runx2 and osteopontin. High phosphate also induced Klf4 expression, although it did not phosphorylate Elk-1. In response to high phosphate, Klf4 selectively bound to the promoter regions of SMC differentiation marker genes. Of importance, siRNA-mediated knockdown of Klf4 blunted high phosphate-induced suppression of SMC differentiation marker genes, as well as increases in expression of osteogenic genes and calcium deposition. Klf4 was also induced markedly in the calcified aorta of adenine-induced uremic rats. Results provide novel evidence that Klf4 mediates high phosphate-induced conversion of SMCs into osteogenic cells.
Figures

References
-
- Tonelli M., Wiebe N., Culleton B., House A., Rabbat C., Fok M., McAlister F., Garg A. X. (2006) Chronic kidney disease and mortality risk: a systematic review. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 17, 2034–2047 - PubMed
-
- London G. M., Guérin A. P., Marchais S. J., Métivier F., Pannier B., Adda H. (2003) Arterial media calcification in end-stage renal disease: impact on all-cause and cardiovascular mortality. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 18, 1731–1740 - PubMed
-
- Moe S. M., O'Neill K. D., Duan D., Ahmed S., Chen N. X., Leapman S. B., Fineberg N., Kopecky K. (2002) Medial artery calcification in ESRD patients is associated with deposition of bone matrix proteins. Kidney Int. 61, 638–647 - PubMed
-
- Shioi A., Nishizawa Y., Jono S., Koyama H., Hosoi M., Morii H. (1995) β-Glycerophosphate accelerates calcification in cultured bovine vascular smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 15, 2003–2009 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

