SOX2 redirects the developmental fate of the intestinal epithelium toward a premature gastric phenotype
- PMID: 22679103
- PMCID: PMC3523556
- DOI: 10.1093/jmcb/mjs030
SOX2 redirects the developmental fate of the intestinal epithelium toward a premature gastric phenotype
Abstract
Various factors play an essential role in patterning the digestive tract. During development, Sox2 and Cdx2 are exclusively expressed in the anterior and the posterior parts of the primitive gut, respectively. However, it is unclear whether these transcription factors influence each other in determining specification of the naïve gut endoderm. We therefore investigated whether Sox2 redirects the fate of the prospective intestinal part of the primitive gut. Ectopic expression of Sox2 in the posterior region of the primitive gut caused anteriorization of the gut toward a gastric-like phenotype. Sox2 activated the foregut transcriptional program, in spite of sustained co-expression of endogenous Cdx2. However, binding of Cdx2 to its genomic targets and thus its transcriptional activity was strongly reduced. Recent findings indicate that endodermal Cdx2 is required to initiate the intestinal program and to suppress anterior cell fate. Our findings suggest that reduced Cdx2 expression by itself is not sufficient to cause anteriorization, but that Sox2 expression is also required. Moreover, it indicates that the balance between Sox2 and Cdx2 function is essential for proper specification of the primitive gut and that Sox2 may overrule the initial patterning of the primitive gut, emphasizing the plasticity of the primitive gut.
Figures

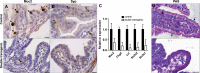

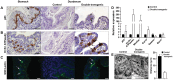
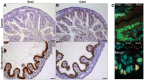

Similar articles
-
Sox2 expression is maintained while gastric phenotype is completely lost in Cdx2-induced intestinal metaplastic mucosa.Differentiation. 2011 Feb;81(2):92-8. doi: 10.1016/j.diff.2010.10.002. Epub 2010 Oct 30. Differentiation. 2011. PMID: 21036460
-
Cdx2 initiates histodifferentiation of the midgut endoderm.FEBS Lett. 2008 Jul 23;582(17):2555-60. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2008.06.024. Epub 2008 Jun 23. FEBS Lett. 2008. PMID: 18577384
-
Disturbed balance between SOX2 and CDX2 in human vitelline duct anomalies and intestinal duplications.Virchows Arch. 2013 May;462(5):515-22. doi: 10.1007/s00428-013-1405-5. Epub 2013 Apr 9. Virchows Arch. 2013. PMID: 23568430
-
Intestinal development and differentiation.Exp Cell Res. 2011 Nov 15;317(19):2702-10. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2011.09.006. Epub 2011 Sep 24. Exp Cell Res. 2011. PMID: 21978911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of embryonic stomach development.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017 Jun;66:36-42. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.02.004. Epub 2017 Feb 24. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 28238948 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Kruppel-like factor 5 controls villus formation and initiation of cytodifferentiation in the embryonic intestinal epithelium.Dev Biol. 2013 Mar 15;375(2):128-39. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.12.010. Epub 2012 Dec 22. Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 23266329 Free PMC article.
-
Roles and action mechanisms of bile acid-induced gastric intestinal metaplasia: a review.Cell Death Discov. 2022 Apr 4;8(1):158. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-00962-1. Cell Death Discov. 2022. PMID: 35379788 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aberrant SOX2 expression in colorectal cancers does not correlate with mucinous differentiation and gastric mucin MUC5AC expression.Virchows Arch. 2014 Oct;465(4):395-400. doi: 10.1007/s00428-014-1638-y. Epub 2014 Aug 10. Virchows Arch. 2014. PMID: 25108707
-
Identification of a neural development gene expression signature in colon cancer stem cells reveals a role for EGR2 in tumorigenesis.iScience. 2022 May 31;25(7):104498. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104498. eCollection 2022 Jul 15. iScience. 2022. PMID: 35720265 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancer, transcriptional, and cell fate plasticity precedes intestinal determination during endoderm development.Genes Dev. 2018 Nov 1;32(21-22):1430-1442. doi: 10.1101/gad.318832.118. Epub 2018 Oct 26. Genes Dev. 2018. PMID: 30366903 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beck F., Erler T., Russell A., et al. Expression of Cdx-2 in the mouse embryo and placenta: possible role in patterning of the extra-embryonic membranes. Dev. Dyn. 1995;204:219–227. - PubMed
-
- Benahmed F., Gross I., Gaunt S.J., et al. Multiple regulatory regions control the complex expression pattern of the mouse Cdx2 homeobox gene. Gastroenterology. 2008;135:1238–1247. 1247.e1–1247.e3. - PubMed
-
- Chawengsaksophak K., James R., Hammond V.E., et al. Homeosis and intestinal tumours in Cdx2 mutant mice. Nature. 1997;386:84–87. - PubMed
-
- Darbas A., Jaegle M., Walbeehm E., et al. Cell autonomy of the mouse claw paw mutation. Dev. Biol. 2004;272:470–482. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

