Modulation of cardiac contractility by the phospholamban/SERCA2a regulatome
- PMID: 22679139
- PMCID: PMC3392125
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.259754
Modulation of cardiac contractility by the phospholamban/SERCA2a regulatome
Abstract
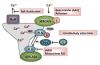
Heart disease remains the leading cause of death and disability in the Western world. Current therapies aim at treating the symptoms rather than the subcellular mechanisms, underlying the etiology and pathological remodeling in heart failure. A universal characteristic, contributing to the decreased contractile performance in human and experimental failing hearts, is impaired calcium sequestration into the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR). SR calcium uptake is mediated by a Ca(2+)-ATPase (SERCA2), whose activity is reversibly regulated by phospholamban (PLN). Dephosphorylated PLN is an inhibitor of SERCA and phosphorylation of PLN relieves this inhibition. However, the initial simple view of a PLN/SERCA regulatory complex has been modified by our recent identification of SUMO, S100 and the histidine-rich Ca-binding protein as regulators of SERCA activity. In addition, PLN activity is regulated by 2 phosphoproteins, the inhibitor-1 of protein phosphatase 1 and the small heat shock protein 20, which affect the overall SERCA-mediated Ca-transport. This review will highlight the regulatory mechanisms of cardiac contractility by the multimeric SERCA/PLN-ensemble and the potential for new therapeutic avenues targeting this complex by using small molecules and gene transfer methods.
Figures





References
-
- MacLennan DH, Abu-Abed M, Kang C. Structure-function relationships in Ca2+ cycling proteins. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2002;34:897–918. - PubMed
-
- He H, Giordano FJ, Hilal-Dandan R, Choi DJ, Rockman HA, McDonough PM, Bluhm WF, Meyer M, Sayen MR, Swanson E, Dillmann WH. Overexpression of the rat sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase gene in the heart of transgenic mice accelerates calcium transients and cardiac relaxation. J Clin Invest. 1997;100:380–9. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baker DL, Hashimoto K, Grupp IL, Ji Y, Reed T, Loukianov E, Grupp G, Bhagwhat A, Hoit B, Walsh R, Marban E, Periasamy M. Targeted overexpression of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase increases cardiac contractility in transgenic mouse hearts. Circ Res. 1998;83:1205–14. - PubMed
-
- Vetter R, Rehfeld U, Reissfelder C, Weiss W, Wagner KD, Gunther J, Hammes A, Tschope C, Dillmann W, Paul M. Transgenic overexpression of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ATPase improves reticular Ca2+ handling in normal and diabetic rat hearts. Faseb J. 2002;16:1657–9. - PubMed
-
- Periasamy M, Reed TD, Liu LH, Ji Y, Loukianov E, Paul RJ, Nieman ML, Riddle T, Duffy JJ, Doetschman T, Lorenz JN, Shull GE. Impaired cardiac performance in heterozygous mice with a null mutation in the sacro(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase isoform 2 (SERCA2) gene. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:2556–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HL-26057/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL088434/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL093183/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL100396/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL088434/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL080498/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL080498/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P20 HL100396/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL083156/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL083156/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL064018/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL093183/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL026057/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201000045C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-64018/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL026057/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

