Effect of Acticoat(®) and Cutinova Hydro(®) on wound healing
- PMID: 22682153
- PMCID: PMC7950677
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1742-481X.2012.01021.x
Effect of Acticoat(®) and Cutinova Hydro(®) on wound healing
Abstract
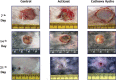
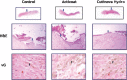
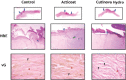
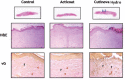
In this study, the effects of the wound-covering materials, Acticoat(®) and Cutinova Hydro(®) , on wound healing have been studied in rabbit models with open and tissue-lost wounds with full-thickness flank excisions. Rabbits were used as subjects with three groups of four rabbits each, and trial periods of 7, 14 and 21{\uns}days. Four circular wounds, of 1.5 cm diameter were made two on the right (one of them control) and two on the left (one of them control) of the dorsal sides of the abdomen. Acticoat(®) and Cutinova Hydro(®) were applied on the wounds with suture for a period of 21 days and one each placed on the right and left sides as control with gauze. Biopsy specimens were taken from the animals at the end of the research period to check the length of the epithelium, epithelial thickness, size of wounds, wound granulation tissue formation and histopathological evaluation for clarity. The Acticoat(®) group showed better healing and scar formation compared to the Cutinova Hydro(®) group by macroscopic examination. Epithelial wound length and clarity in terms of statistical difference occurred on day 21 (P <0.05); while the length of the wound epithelium decreased patency, epithelial thickness on days~7, 14 and 21, showed no statistical differences (P >0.05). As a result, the Acticoat(®) wound dressing was determined as a more reliable for the early wound healing. This study has shown the short-term clinical benefits of hydroactive, polyurethane dressings in the management of acute wounds. However, longer periods of wound healing procedure should be planned for reliable and safe results of wound dressing. It has also been concluded that microbiological analyses should be included for more robust and reliable comparisons.
Keywords: Acticoat®; Clinical-pathological observation; Cutinova Hydro®; Wound healing.
© 2012 The Authors. International Wound Journal © 2012 John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Medicalhelplines.com Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A silver-coated antimicrobial barrier dressing used postoperatively on meshed autografts: a dressing comparison study.J Burn Care Res. 2007 Sep-Oct;28(5):715-9. doi: 10.1097/BCR.0B013E318148C9E4. J Burn Care Res. 2007. PMID: 17667837 Clinical Trial.
-
A prospective, randomized trial of Acticoat versus silver sulfadiazine in the treatment of partial-thickness burns: which method is less painful?J Burn Care Rehabil. 2005 Jul-Aug;26(4):344-7. doi: 10.1097/01.bcr.0000170119.87879.ca. J Burn Care Rehabil. 2005. PMID: 16006842 Clinical Trial.
-
Evaluation of cytotoxicity and antimicrobial activity of Acticoat Burn Dressing for management of microbial contamination in cultured skin substitutes grafted to athymic mice.J Burn Care Rehabil. 2005 May-Jun;26(3):238-46. J Burn Care Rehabil. 2005. PMID: 15879745
-
Use of Acticoat dressings in burns: what is the evidence?Burns. 2010 Sep;36(6):751-8. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2009.04.008. Epub 2010 Mar 25. Burns. 2010. PMID: 20346592 Review.
-
Comparative study of Silver Sulfadiazine with other materials for healing and infection prevention in burns: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Burns. 2019 Mar;45(2):282-292. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2018.05.014. Epub 2018 Jun 11. Burns. 2019. PMID: 29903603
Cited by
-
Acticoat™ stimulates inflammation, but does not delay healing, in acute full-thickness excisional wounds.Int Wound J. 2016 Dec;13(6):1344-1348. doi: 10.1111/iwj.12525. Epub 2015 Nov 11. Int Wound J. 2016. PMID: 26561384 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arıcan M, Ozturk A. A clinical study using collagenase enzyme in the treatment of open or infected wounds. Eurasian J Vet Sci 1999;15:153–8.
-
- Innes ME, Umraw N, Fish JS, Gomez M, Cartotto RC. The use of silver coated dressings on donor site wounds: a prospective, controlled matched pair study. Burns 2001;27:621–7. - PubMed
-
- Ogurtan Z, Hatipoglu F, Ceylan C. The effect of Alkanna tinctoria Tausch on burn wound healing in rabbits. Dtsch Tierarztl Wochenschr 2002;109:481–5. - PubMed
-
- Wynne R, Holsworth L, Flavell O. Effect of three wound dressings on infection, healing comfort, and cost in patients with sternotomy wounds. Chest 2004;125:43–9. - PubMed
-
- Yavru N, Koc Y, Arıcan M, Doğruer Y. The effect of granulated sugar application on healing in the treatment of infected wounds and abscesses. Eurasian J Vet Sci 1992;8:64–8.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

