The sedoheptulose kinase CARKL directs macrophage polarization through control of glucose metabolism
- PMID: 22682222
- PMCID: PMC3370649
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2012.04.023
The sedoheptulose kinase CARKL directs macrophage polarization through control of glucose metabolism
Abstract
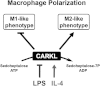
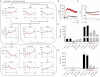
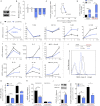
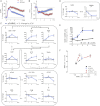
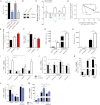
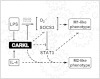
Immune cells are somewhat unique in that activation responses can alter quantitative phenotypes upwards of 100,000-fold. To date little is known about the metabolic adaptations necessary to mount such dramatic phenotypic shifts. Screening for novel regulators of macrophage activation, we found nonprotein kinases of glucose metabolism among the most enriched classes of candidate immune modulators. We find that one of these, the carbohydrate kinase-like protein CARKL, is rapidly downregulated in vitro and in vivo upon LPS stimulation in both mice and humans. Interestingly, CARKL catalyzes an orphan reaction in the pentose phosphate pathway, refocusing cellular metabolism to a high-redox state upon physiological or artificial downregulation. We find that CARKL-dependent metabolic reprogramming is required for proper M1- and M2-like macrophage polarization and uncover a rate-limiting requirement for appropriate glucose flux in macrophage polarization.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Polarizing macrophages through reprogramming of glucose metabolism.Cell Metab. 2012 Jun 6;15(6):793-5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2012.05.008. Cell Metab. 2012. PMID: 22682218
References
-
- Chen Y.J., Hsu K.W., Tsai J.N., Hung C.H., Kuo T.C., Chen Y.L. Involvement of protein kinase C in the inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production by thapsigargin in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2005;37:2574–2585. - PubMed
-
- Demas G.E., Chefer V., Talan M.I., Nelson R.J. Metabolic costs of mounting an antigen-stimulated immune response in adult and aged C57BL/6J mice. Am. J. Physiol. 1997;273:R1631–R1637. - PubMed
-
- Drapier J.C., Hibbs J.B., Jr. Differentiation of murine macrophages to express nonspecific cytotoxicity for tumor cells results in L-arginine-dependent inhibition of mitochondrial iron-sulfur enzymes in the macrophage effector cells. J. Immunol. 1988;140:2829–2838. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

