The NAD(+) precursor nicotinamide riboside enhances oxidative metabolism and protects against high-fat diet-induced obesity
- PMID: 22682224
- PMCID: PMC3616313
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2012.04.022
The NAD(+) precursor nicotinamide riboside enhances oxidative metabolism and protects against high-fat diet-induced obesity
Abstract
As NAD(+) is a rate-limiting cosubstrate for the sirtuin enzymes, its modulation is emerging as a valuable tool to regulate sirtuin function and, consequently, oxidative metabolism. In line with this premise, decreased activity of PARP-1 or CD38-both NAD(+) consumers-increases NAD(+) bioavailability, resulting in SIRT1 activation and protection against metabolic disease. Here we evaluated whether similar effects could be achieved by increasing the supply of nicotinamide riboside (NR), a recently described natural NAD(+) precursor with the ability to increase NAD(+) levels, Sir2-dependent gene silencing, and replicative life span in yeast. We show that NR supplementation in mammalian cells and mouse tissues increases NAD(+) levels and activates SIRT1 and SIRT3, culminating in enhanced oxidative metabolism and protection against high-fat diet-induced metabolic abnormalities. Consequently, our results indicate that the natural vitamin NR could be used as a nutritional supplement to ameliorate metabolic and age-related disorders characterized by defective mitochondrial function.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

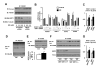
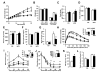
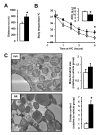
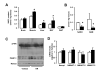
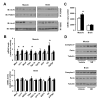
References
-
- Barbosa MT, Soares SM, Novak CM, Sinclair D, Levine JA, Aksoy P, Chini EN. The enzyme CD38 (a NAD glycohydrolase, EC 3.2.2.5) is necessary for the development of diet-induced obesity. FASEB J. 2007;21:3629–3639. - PubMed
-
- Belenky P, Racette FG, Bogan KL, McClure JM, Smith JS, Brenner C. Nicotinamide riboside promotes Sir2 silencing and extends lifespan via Nrk and Urh1/Pnp1/Meu1 pathways to NAD+ Cell. 2007;129:473–484. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

