Phonetically governed voicing onset and offset in preschool children who stutter
- PMID: 22682319
- PMCID: PMC3372869
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jfludis.2012.04.001
Phonetically governed voicing onset and offset in preschool children who stutter
Abstract
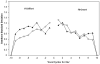
Phonetically governed changes in the fundamental frequency (F₀) of vowels that immediately precede and follow voiceless stop plosives have been found to follow consistent patterns in adults and children as young as four years of age. In the present study, F₀ onset and offset patterns in 14 children who stutter (CWS) and 14 children who do not stutter (CWNS) were investigated to evaluate differences in speech production. Participants produced utterances containing two VCV sequences. F₀ patterns in the last ten vocal cycles in the preceding vowel (voicing offset) and the first ten vocal cycles in the subsequent vowel (voicing onset) were analyzed. A repeated measures ANOVA revealed no group differences between the CWS and CWNS in either voicing onset or offset gestures. Both groups showed patterns of F₀ onset and offset that were consistent with the mature patterns seen in children and adults in previous studies. These findings suggest that in both CWS and CWNS, a mature pattern of voicing onset and offset is present by age 3;6. This study suggests that there is no difference between CWS and CWNS in the coordination of respiratory and laryngeal systems during voicing onset or offset.
Educational objectives: The reader will be able to: (a) discuss the importance of investigating children who stutter close to the onset of stuttering; (b) describe the typical change in F₀ during voicing onset; (c) discuss the potential implications of these results with regard to future research.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Adams M. Voice onsets and segment durations of normal speakers and beginning stutterers. Journal of Fluency Disorders. 1987;12:133–139.
-
- Baken R, Orlikoff R. Changes in vocal fundamental frequency at the segmental level: Control during voiced fricatives. Journal of Speech and Hearing Research. 1988;31:207–211. - PubMed
-
- Caruso A, Conture E, Colton R. Selected temporal parameters of coordination associated with stuttering in children. Journal of Fluency Disorders. 1988;13:57–82.
-
- Chang S, Ohde R, Conture E. Coarticulation and formant transition rate in young children who stutter. Journal of Speech, Language and Hearing Research. 2002;45:676–688. - PubMed
-
- Conture E, Colton R, Gleason J. Selected temporal aspects of coordination during fluent speech of young stutterers. Journal of Speech and Hearing Research. 1988;31:640–653. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

