Time trends in medication use and expenditures in older patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 22682794
- PMCID: PMC3432666
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2011.11.014
Time trends in medication use and expenditures in older patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Background: We sought to examine how expansions in insurance coverage of nonbiologic and biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs affected the access, costs, and health status of older patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
Methods: We identified a nationally representative sample of older adults with rheumatoid arthritis in the 2000-2006 Medicare Current Beneficiary Survey (unweighted n=1051). We examined changes in disease-modifying antirheumatic drug use, self-reported health status, functional status (activities of daily living), and total costs and out-of-pocket costs for medical care and prescription drugs. Tests for time trends were conducted using weighted regressions.
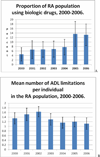
Results: Between 2000 and 2006, the proportion of older adults with rheumatoid arthritis who received biologics tripled (4.6% vs 13.2%, P=.01), whereas the proportion of people who used a nonbiologic did not change. During the same period, the proportion of older patients with rheumatoid arthritis rating their health as excellent/good significantly increased (43.0% in 2000 to 55.6% in 2006; P=.015). Significant improvements occurred in activities of daily living measures of functional status. Total prescription drug costs (in 2006 US dollars) increased from $2645 in 2000 to $4685 in 2006, P=.0001, whereas out-of-pocket prescription costs remained constant ($842 in 2000 vs $832 in 2006; P=.68). Total medical costs did not significantly increase ($16,563 in 2000 vs $19,510 in 2006; P=.07).
Conclusion: Receipt of biologics in older adults with rheumatoid arthritis increased over a period of time when insurance coverage was expanded without increasing patients' out-of-pocket costs. During this time period, concurrent improvements in self-reported health status and functional status suggest improved arthritis care.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
All authors had access to the data and a role in writing the manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Costs of tumor necrosis factor blockers per treated patient using real-world drug data in a managed care population.J Manag Care Pharm. 2013 Oct;19(8):621-30. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2013.19.8.621. J Manag Care Pharm. 2013. PMID: 24074008 Free PMC article.
-
Adalimumab, etanercept, and infliximab utilization patterns and drug costs among rheumatoid arthritis patients.J Med Econ. 2012;15(2):332-9. doi: 10.3111/13696998.2011.649325. Epub 2012 Jan 6. J Med Econ. 2012. PMID: 22168788
-
Estimated medication costs of primary TNFα antagonist failure in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Joint Bone Spine. 2012 Jul;79(4):421-2. doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2012.01.017. Epub 2012 Apr 17. Joint Bone Spine. 2012. PMID: 22512937 No abstract available.
-
Review of eight pharmacoeconomic studies of the value of biologic DMARDs (adalimumab, etanercept, and infliximab) in the management of rheumatoid arthritis.J Manag Care Pharm. 2006 Sep;12(7):555-69. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2006.12.7.555. J Manag Care Pharm. 2006. PMID: 16981801 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Therapeutic efficacy and the adverse effects of newly developed biological agents for rheumatoid arthritis].Nihon Naika Gakkai Zasshi. 2004 Jan 10;93(1):153-60. doi: 10.2169/naika.93.153. Nihon Naika Gakkai Zasshi. 2004. PMID: 14968591 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Discussing Out-of-Pocket Expenses During Clinical Appointments: An Observational Study of Patient-Psychiatrist Interactions.Psychiatr Serv. 2017 Jun 1;68(6):610-617. doi: 10.1176/appi.ps.201600275. Epub 2017 Mar 15. Psychiatr Serv. 2017. PMID: 28292225 Free PMC article.
-
Population Variations in Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment and Outcomes, Northern California, 1998-2009.Perm J. 2016 Winter;20(1):4-12. doi: 10.7812/TPP/15-028. Epub 2015 Dec 21. Perm J. 2016. PMID: 26694020 Free PMC article.
-
Medical Care Costs Associated With Rheumatoid Arthritis in the US: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2018 Oct;70(10):1431-1438. doi: 10.1002/acr.23512. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2018. PMID: 29316377 Free PMC article.
-
Management of inflammatory rheumatic conditions in the elderly.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019 May 1;58(5):748-764. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/key165. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019. PMID: 29982766 Free PMC article. Review.
-
What Strategies Do Physicians and Patients Discuss to Reduce Out-of-Pocket Costs? Analysis of Cost-Saving Strategies in 1,755 Outpatient Clinic Visits.Med Decis Making. 2016 Oct;36(7):900-10. doi: 10.1177/0272989X15626384. Epub 2016 Jan 19. Med Decis Making. 2016. PMID: 26785714 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saag KG, Teng GG, Patkar NM, Anuntiyo J, Finney C, Curtis JR, et al. American College of Rheumatology 2008 recommendations for the use of nonbiologic and biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;59(6):762–784. - PubMed
-
- Breedveld FC, Weisman MH, Kavanaugh AF, Cohen SB, Pavelka K, van Vollenhoven R, et al. The PREMIER study: A multicenter, randomized, double-blind clinical trial of combination therapy with adalimumab plus methotrexate versus methotrexate alone or adalimumab alone in patients with early, aggressive rheumatoid arthritis who had not had previous methotrexate treatment. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54(1):26–37. - PubMed
-
- Emery P, Breedveld FC, Hall S, Durez P, Chang DJ, Robertson D, et al. Comparison of methotrexate monotherapy with a combination of methotrexate and etanercept in active, early, moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis (COMET): a randomised, double-blind, parallel treatment trial. Lancet. 2008;372(9636):375–382. - PubMed
-
- St Clair EW, van der Heijde DM, Smolen JS, Maini RN, Bathon JM, Emery P, et al. Combination of infliximab and methotrexate therapy for early rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized, controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50(11):3432–3443. - PubMed
-
- Berard A, Solomon DH, Avorn J. Patterns of drug use in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2000;27(7):1648–1655. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical