Direct reprogramming of mouse and human fibroblasts into multipotent neural stem cells with a single factor
- PMID: 22683203
- PMCID: PMC3399516
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2012.05.018
Direct reprogramming of mouse and human fibroblasts into multipotent neural stem cells with a single factor
Abstract
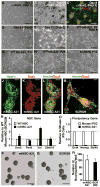
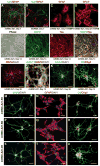
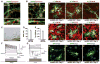
The generation of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) and induced neuronal cells (iNCs) from somatic cells provides new avenues for basic research and potential transplantation therapies for neurological diseases. However, clinical applications must consider the risk of tumor formation by iPSCs and the inability of iNCs to self-renew in culture. Here we report the generation of induced neural stem cells (iNSCs) from mouse and human fibroblasts by direct reprogramming with a single factor, Sox2. iNSCs express NSC markers and resemble wild-type NSCs in their morphology, self-renewal, ability to form neurospheres, and gene expression profiles. Cloned iNSCs differentiate into several types of mature neurons, as well as astrocytes and oligodendrocytes, indicating multipotency. Implanted iNSCs can survive and integrate in mouse brains and, unlike iPSC-derived NSCs, do not generate tumors. Thus, self-renewable and multipotent iNSCs without tumorigenic potential can be generated directly from fibroblasts by reprogramming.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Bylund M, Andersson E, Novitch BG, Muhr J. Vertebrate neurogenesis is counteracted by Sox1–3 activity. Nat Neurosci. 2003;6:1162–1168. - PubMed
-
- Caiazzo M, Dell’Anno MT, Dvoretskova E, Lazarevic D, Taverna S, Leo D, Sotnikova TD, Menegon A, Roncaglia P, Colciago G, et al. Direct generation of functional dopaminergic neurons from mouse and human fibroblasts. Nature. 2011;476:224–227. - PubMed
-
- Dimos JT, Rodolfa KT, Niakan KK, Weisenthal LM, Mitsumoto H, Chung W, Croft GF, Saphier G, Leibel R, Goland R, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cells generated from patients with ALS can be differentiated into motor neurons. Science. 2008;321:1218–1221. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

