Bone marrow failure in Fanconi anemia is triggered by an exacerbated p53/p21 DNA damage response that impairs hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells
- PMID: 22683204
- PMCID: PMC3392433
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2012.05.013
Bone marrow failure in Fanconi anemia is triggered by an exacerbated p53/p21 DNA damage response that impairs hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells
Abstract
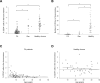
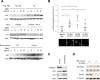
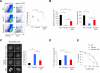
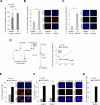
Fanconi anemia (FA) is an inherited DNA repair deficiency syndrome. FA patients undergo progressive bone marrow failure (BMF) during childhood, which frequently requires allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. The pathogenesis of this BMF has been elusive to date. Here we found that FA patients exhibit a profound defect in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) that is present before the onset of clinical BMF. In response to replicative stress and unresolved DNA damage, p53 is hyperactivated in FA cells and triggers a late p21(Cdkn1a)-dependent G0/G1 cell-cycle arrest. Knockdown of p53 rescued the HSPC defects observed in several in vitro and in vivo models, including human FA or FA-like cells. Taken together, our results identify an exacerbated p53/p21 "physiological" response to cellular stress and DNA damage accumulation as a central mechanism for progressive HSPC elimination in FA patients, and have implications for clinical care.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Comment in
-
Heightened DNA damage response impairs hematopoiesis in Fanconi anemia.Haematologica. 2012 Aug;97(8):1117. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2012.073643. Haematologica. 2012. PMID: 22855843 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bagby GC, Meyers G. Bone marrow failure as a risk factor for clonal evolution: prospects for leukemia prevention. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2007;2007:40–46. - PubMed
-
- Barroca V, Mouthon MA, Lewandowski D, Brunet de la Grange P, Gauthier LR, Pflumio F, Boussin FD, Arwert F, Riou L, Allemand I, et al. Impaired functionality and homing of Fancg-deficient hematopoietic stem cells. Hum Mol Genet. 2011 - PubMed
-
- Berns K, Hijmans EM, Mullenders J, Brummelkamp TR, Velds A, Heimerikx M, Kerkhoven RM, Madiredjo M, Nijkamp W, Weigelt B, et al. A large-scale RNAi screen in human cells identifies new components of the p53 pathway. Nature. 2004;428:431–437. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

