Novel protective mechanisms for S-adenosyl-L-methionine against acetaminophen hepatotoxicity: improvement of key antioxidant enzymatic function
- PMID: 22683606
- PMCID: PMC3398222
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2012.05.018
Novel protective mechanisms for S-adenosyl-L-methionine against acetaminophen hepatotoxicity: improvement of key antioxidant enzymatic function
Abstract
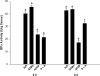
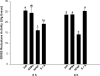
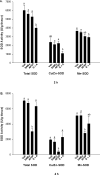
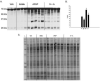
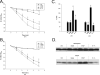
Acetaminophen (APAP) overdose leads to severe hepatotoxicity, increased oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAMe) protects against APAP toxicity at a mmol/kg equivalent dose to N-acetylcysteine (NAC). SAMe acts as a principle biological methyl donor and participates in polyamine synthesis which increase cell growth and has a role in mitochondrial protection. The purpose of the current study tested the hypothesis that SAMe protects against APAP toxicity by maintaining critical antioxidant enzymes and markers of oxidative stress. Male C57Bl/6 mice were treated with vehicle (Veh; water 15 ml/kg, ip), SAMe (1.25 mmol/kg, ip), APAP (250 mg/kg, ip), and SAMe+APAP (SAMe given 1 h following APAP). Liver was collected 2 and 4 h following APAP administration; mitochondrial swelling as well as hepatic catalase, glutathione peroxidase (GPx), glutathione reductase, and both Mn- and Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase (SOD) enzyme activity were evaluated. Mitochondrial protein carbonyl, 3-nitrotyrosine cytochrome c leakage were analyzed by Western blot. SAMe significantly increased SOD, GPx, and glutathione reductase activity at 4 h following APAP overdose. SAMe greatly reduced markers of oxidative stress and cytochrome C leakage following APAP overdose. Our studies also demonstrate that a 1.25 mmol/kg dose of SAMe does not inhibit CYP 2E1 enzyme activity. The current study identifies a plausible mechanism for the decreased oxidative stress observed when SAMe is given following APAP.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


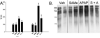

References
-
- Adamson GM, Harman AW. A role for the glutathione peroxidase/reductase enzyme system in the protection from paracetamol toxicity in isolated mouse hepatocytes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989;38:3323–3330. - PubMed
-
- Andersson BS, Rundgren M, Nelson SD, Harder S. N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine-induced changes in the energy metabolism in hepatocytes. Chem Biol Interact. 1990;75:201–211. - PubMed
-
- Anundi I, Lahteenmaki T, Rundgren M, Moldeus P, Lindros KO. Zonation of acetaminophen metabolism and cytochrome P450 2E1-mediated toxicity studied in isolated periportal and perivenous hepatocytes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1993;45:1251–1259. - PubMed
-
- Bailey SM, Robinson G, Pinner A, Chamlee L, Ulasova E, Pompilius M, Page GP, Chhieng D, Jhala N, Landar A, Kharbanda KK, Ballinger S, Darley-Usmar V. S-adenosylmethionine prevents chronic alcohol-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in the rat liver. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2006;291:G857–867. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

