The zinc-finger domains of PARP1 cooperate to recognize DNA strand breaks
- PMID: 22683995
- PMCID: PMC4826610
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.2335
The zinc-finger domains of PARP1 cooperate to recognize DNA strand breaks
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: The zinc-finger domains of PARP1 cooperate to recognize DNA strand breaks.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015 Aug;22(8):645. doi: 10.1038/nsmb0815-645a. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 26243658 No abstract available.
Abstract
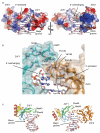
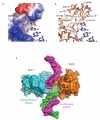
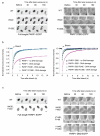
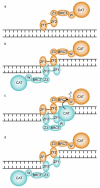
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1) is a primary DNA damage sensor whose (ADP-ribose) polymerase activity is acutely regulated by interaction with DNA breaks. Upon activation at sites of DNA damage, PARP1 modifies itself and other proteins by covalent addition of long, branched polymers of ADP-ribose, which in turn recruit downstream DNA repair and chromatin remodeling factors. PARP1 recognizes DNA damage through its N-terminal DNA-binding domain (DBD), which consists of a tandem repeat of an unusual zinc-finger (ZnF) domain. We have determined the crystal structure of the human PARP1-DBD bound to a DNA break. Along with functional analysis of PARP1 recruitment to sites of DNA damage in vivo, the structure reveals a dimeric assembly whereby ZnF1 and ZnF2 domains from separate PARP1 molecules form a strand-break recognition module that helps activate PARP1 by facilitating its dimerization and consequent trans-automodification.
Figures


Comment in
-
PARP pairs up to PARsylate.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012 Jul 5;19(7):660-1. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2306. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22767236 No abstract available.
References
-
- Pion E, et al. DNA-induced dimerization of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 triggers its activation. Biochemistry. 2005;44:14670–81. - PubMed
-
- Kirsten E, Kun E, Mendeleyev J, Ordahl CP. Activity assays for poly-ADP ribose polymerase. Methods Mol Biol. 2004;287:137–49. - PubMed
-
- Huang K, et al. Analysis of nucleotide sequence-dependent DNA binding of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase in a purified system. Biochemistry. 2004;43:217–23. - PubMed
-
- Shall S, de Murcia G. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1: what have we learned from the deficient mouse model? Mutation Research-Dna Repair. 2000;460:1–15. - PubMed
-
- Ame JC, Spenlehauer C, de Murcia G. The PARP superfamily. Bioessays. 2004;26:882–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

