Stable functionalization of small semiconducting polymer dots via covalent cross-linking and their application for specific cellular imaging
- PMID: 22684783
- PMCID: PMC3433747
- DOI: 10.1002/adma.201201245
Stable functionalization of small semiconducting polymer dots via covalent cross-linking and their application for specific cellular imaging
Abstract
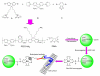
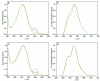
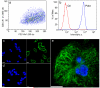
A facile cross-linking strategy covalently links functional molecules to semiconducting polymer dots (Pdots) while simultaneously providing functional groups for biomolecular conjugation. In addition to greatly enhanced stability, the formed Pdots are small (<10 nm), which can be difficult to achieve with current methods but is highly desirable for most biological applications. These characteristics are significant for improving labeling efficiency and sensitivity in cellular assays that employ Pdots.
Copyright © 2012 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

