Cloning, production, and functional expression of the bacteriocin enterocin A, produced by Enterococcus faecium T136, by the yeasts Pichia pastoris, Kluyveromyces lactis, Hansenula polymorpha, and Arxula adeninivorans
- PMID: 22685156
- PMCID: PMC3406115
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00530-12
Cloning, production, and functional expression of the bacteriocin enterocin A, produced by Enterococcus faecium T136, by the yeasts Pichia pastoris, Kluyveromyces lactis, Hansenula polymorpha, and Arxula adeninivorans
Abstract
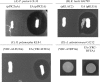
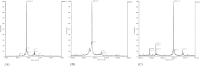
The bacteriocin enterocin A (EntA) produced by Enterococcus faecium T136 has been successfully cloned and produced by the yeasts Pichia pastoris X-33EA, Kluyveromyces lactis GG799EA, Hansenula polymorpha KL8-1EA, and Arxula adeninivorans G1212EA. Moreover, P. pastoris X-33EA and K. lactis GG799EA produced EntA in larger amounts and with higher antimicrobial and specific antimicrobial activities than the EntA produced by E. faecium T136.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Use of synthetic genes for cloning, production and functional expression of the bacteriocins enterocin A and bacteriocin E 50-52 by Pichia pastoris and Kluyveromyces lactis.Mol Biotechnol. 2014 Jun;56(6):571-83. doi: 10.1007/s12033-014-9731-7. Mol Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 24510220
-
Cloning, production and expression of the bacteriocin enterocin A produced by Enterococcus faecium PLBC21 in Lactococcus lactis.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007 Sep;76(3):667-75. doi: 10.1007/s00253-007-1044-3. Epub 2007 Jun 27. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007. PMID: 17594089
-
Production of enterocin P, an antilisterial pediocin-like bacteriocin from Enterococcus faecium P13, in Pichia pastoris.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005 Jul;49(7):3004-8. doi: 10.1128/AAC.49.7.3004-3008.2005. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005. PMID: 15980385 Free PMC article.
-
New yeast expression platforms based on methylotrophic Hansenula polymorpha and Pichia pastoris and on dimorphic Arxula adeninivorans and Yarrowia lipolytica - a comparison.FEMS Yeast Res. 2005 Nov;5(11):1079-96. doi: 10.1016/j.femsyr.2005.06.004. Epub 2005 Aug 24. FEMS Yeast Res. 2005. PMID: 16144775 Review.
-
Application of yeasts in gene expression studies: a comparison of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Hansenula polymorpha and Kluyveromyces lactis -- a review.Gene. 1997 Apr 29;190(1):87-97. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(97)00020-6. Gene. 1997. PMID: 9185853 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhanced bactericidal effect of enterocin A in combination with thyme essential oils against L. monocytogenes and E. coli O157:H7.J Food Sci Technol. 2015 Apr;52(4):2148-56. doi: 10.1007/s13197-013-1214-5. Epub 2013 Dec 3. J Food Sci Technol. 2015. PMID: 25829595 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of Caseicin from Lacticaseibacillus casei and Lacticaseibacillus zeae Provides Insight into Antilisterial Class IIa Bacteriocins.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2024 Aug 13. doi: 10.1007/s12602-024-10341-0. Online ahead of print. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2024. PMID: 39136873
-
Cloning strategies for heterologous expression of the bacteriocin enterocin A by Lactobacillus sakei Lb790, Lb. plantarum NC8 and Lb. casei CECT475.Microb Cell Fact. 2015 Oct 15;14:166. doi: 10.1186/s12934-015-0346-x. Microb Cell Fact. 2015. PMID: 26471395 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning and expression of synthetic genes encoding the broad antimicrobial spectrum bacteriocins SRCAM 602, OR-7, E-760, and L-1077, by recombinant Pichia pastoris.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:767183. doi: 10.1155/2015/767183. Epub 2015 Mar 2. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 25821820 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization, yield optimization, scale up and biopreservative potential of fermencin SA715, a novel bacteriocin from Lactobacillus fermentum GA715 of goat milk origin.Microb Cell Fact. 2018 Aug 13;17(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s12934-018-0972-1. Microb Cell Fact. 2018. PMID: 30103750 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aymerich MT, et al. 2000. Application of enterocins as biopreservatives against Listeria innocua in meat products. J. Food Prot. 63:721–726 - PubMed
-
- Beaulieu L, et al. 2005. Production of pediocin PA-1 in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris reveals unexpected inhibition of its biological activity due to the presence of collagen-like material. Protein Expr. Purif. 43:111–125 - PubMed
-
- Böer E, Steinborn G, Kunze G, Gellissen G. 2007. Yeast expression platforms. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 77:513–523 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

