Nanoparticle-based therapy in an in vivo microRNA-155 (miR-155)-dependent mouse model of lymphoma
- PMID: 22685206
- PMCID: PMC3387084
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1201516109
Nanoparticle-based therapy in an in vivo microRNA-155 (miR-155)-dependent mouse model of lymphoma
Abstract
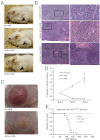
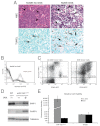
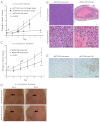
MicroRNA-155 (miR-155) is an oncogenic microRNA that regulates several pathways involved in cell division and immunoregulation. It is overexpressed in numerous cancers, is often correlated with poor prognosis, and is thus a key target for future therapies. In this work we show that overexpression of miR-155 in lymphoid tissues results in disseminated lymphoma characterized by a clonal, transplantable pre-B-cell population of neoplastic lymphocytes. Withdrawal of miR-155 in mice with established disease results in rapid regression of lymphadenopathy, in part because of apoptosis of the malignant lymphocytes, demonstrating that these tumors are dependent on miR-155 expression. We show that systemic delivery of antisense peptide nucleic acids encapsulated in unique polymer nanoparticles inhibits miR-155 and slows the growth of these "addicted" pre-B-cell tumors in vivo, suggesting a promising therapeutic option for lymphoma/leukemia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Babar IA, Slack FJ, Weidhaas JB. miRNA modulation of the cellular stress response. Future Oncol. 2008;4:289–298. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Garcia I, Miska EA. MicroRNA functions in animal development and human disease. Development. 2005;132:4653–4662. - PubMed
-
- Bushati N, Cohen SM. microRNA functions. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2007;23:175–205. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

